FRNC, HFFR, LS0H, LSZH flame-retardant, halogen-free cables
Halogen-free cables are a required staple in a vast number of industrial and infrastructural applications. Over time, different labels for these cables have been established, such as FRNC, HFFR, LS0H, or LSZH. But how meaningful are these abbreviations, and what are the benefits of halogen-free cables compared to products containing halogens? Let HELUKABEL explain.
1. What is halogen in flame-retardant cables?

Halogen-free cables are a required staple in a vast number of industrial and infrastructural applications. Over time, different labels for these cables have been established, such as FRNC, HFFR, LS0H, or LSZH. But how meaningful are these abbreviations, and what are the benefits of halogen-free cables compared to products containing halogens? Let HELUKABEL explain.
Halogens (which means "to form salt") include the chemical elements chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), fluorine (F), and iodine (I). When manufacturing cables, these are used to make certain core insulation and sheathing materials flame retardant. This is where chlorine (which is a component of PVC plastic or chloroprene rubber) and fluorine (which is found in the high-temperature materials FEP, PTFE, and ETFE) come into play. Even bromine is used in flame retardants for cables and wires.
>>See more: HELUKABEL's flame-retardant cables for industrial applications
2. Significance of flame-retardant cables

2.1 What is halogen-free?
The problem is that halogens burn extremely aggressively and emit noxious fumes when ignited. They produce halogen halides which turn into acids when they come into contact with moisture and can cause acid burns in the respiratory tract. Furthermore, the acids that are released can cause metal parts to corrode, damaging machines and even the rebar reinforcements of concrete in buildings. This can result in the need for time-consuming and costly decontamination efforts.
The flame retardancy of cables and wires is, of course, an important criterion for fire prevention measures. There are also a number of applications that explicitly require halogen-free products, which means cables and wires consisting of materials that are free of chlorine, bromine, fluorine, and iodine. Should these cables be ignited, they produce much less acid and smoke, and are less toxic, which substantially reduces the consequential damage to people, buildings, and machines. Poisonous gases such as carbon monoxide are, however, still emitted when halogen-free cables are ignited.
2.2 Applications of flame-retardant, halogen-free cables
Halogen-free cables and wires are required, for example, in buildings where people gather and where valuable material assets must be protected. Examples for this are:
- Building technology: In public buildings such as offices, shopping centres, schools, hospitals, and airports, strong fire and health risk prevention ordinances are in place. Most of the cables and wires in these places are fixed in their installation and do not need to fulfil any special chemical or mechanical requirements. PE or PP-based plastic mixtures are often used here, which are halogen free and flame-retardant, and produce little smoke or toxic gas. They must also often pass bundle burning tests.
- Industrial automation: Machines and plants often require cables and wires with high chemical and mechanical resistance. When used in flexible applications such as in drag chains or in robotics, these loads are especially high. Typically, sheath mixtures based on TPE-O or TPE-U (PUR or Santoprene) are used here. These are also available with halogen-free constructions but are not able to be manufactured to be as flame-retardant or low smoke as cables for building technology.
3. Typical labels for flame-retardant, halogen-free cables
Over the years, different manufacturers, markets, regions, and standards have developed different labels for halogen-free and flame-retardant cables:
3.1 FRNC – Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive cables
FRNC stands for Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive. FRNC cables are engineered to limit the spread of fire, preventing it from reaching other areas. These cables are particularly suited for environments with a high risk of fire where protecting human life and valuable assets is crucial. Additionally, they are halogen-free and do not emit corrosive gases when exposed to fire, making them a safer choice for critical applications.
Some FRNC cables from HELUKABEL:
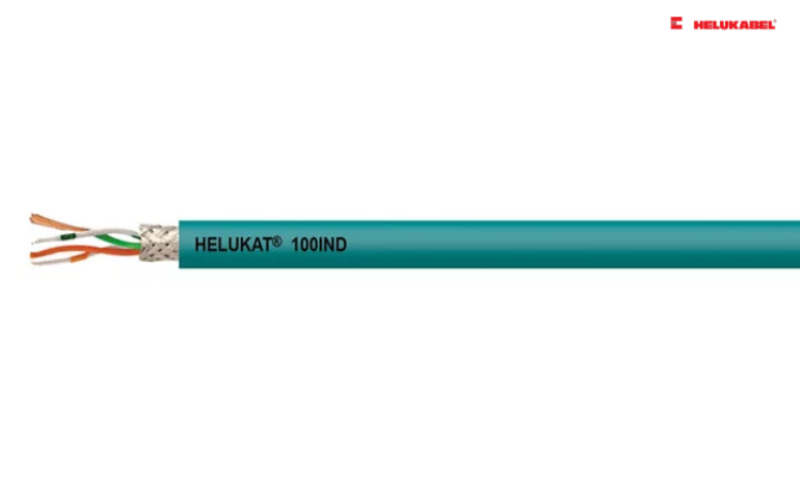
- HELUKAT® 100IND CAT.5 WK SF/UTP X-FRNC FLEX is specially designed for demanding temperature requirements such as in wind turbines. Radiant cross-linking provides improved thermal stability as well as good oil resistance.
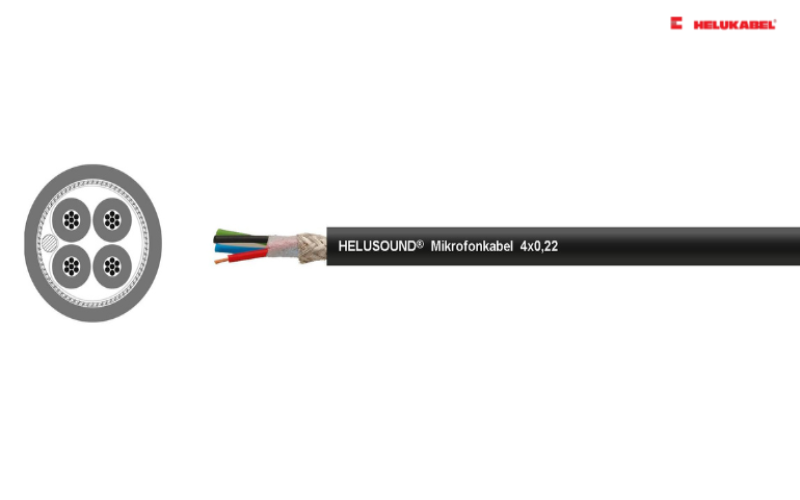
- The 4-core HELUSOUND® microphone cable is star-braided and is suitable for special applications due to its ground wire and braided shielding. For example, it is used as a stereo cable in the field of microphone engineering and professional studios.
- The HELUKAT® 100IND CAT.5e SF/UTP FRNC FLEX is highly flexible.
3.2 HFFR – Halogen Free Flame-Retardant cables
HFFR (Halogen-Free Flame Retardant) cable compound is a material used for the insulation and sheathing of electrical cables. This compound is free of halogens, which helps reduce toxic emissions in the event of a fire. The flame retardants used in HFFR compounds include:
- Aluminum Hydroxide (ATH): ATH decomposes at around 200°C, releasing water vapor and absorbing heat. This process cools the material and helps dilute flammable gases, reducing the spread of fire
- Magnesium Hydroxide (MDH): Similar to ATH, MDH decomposes at approximately 300°C, releasing water vapor and absorbing heat, providing additional fire resistance.
Some HFFR cables from HELUKABEL: NSHXAFÖ 1,8/3 kV, DATAFLAMM®, SiHF/GL-P
3.3 LSZH – Low Smoke Zero Halogen cables
Unlike PVC cables and those made from other compounds, which release dense black smoke, toxic fumes, and acid gases when exposed to fire, LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) cables produce minimal smoke, low levels of toxic fumes, and no acid gases. These cables are essentially halogen-free. As a result, they are commonly specified for indoor use, particularly in public spaces, hazardous environments, and poorly ventilated areas, such as in vehicles, aircraft, railway carriages, and ships. LSZH sheathed cables are also widely used in tunnels and underground rail networks.
3.4 LS0H, LSOH cables
LS0H or LSOH cable are some other abbreviations of LSZH cable, possessing similar characteristics and properties to LSZH cable.
None of these labels, however, deliver concrete information regarding flame retardancy, corrosiveness, toxicity, and light attenuation. Users must therefore pay close attention to the standards listed in the data sheets of each supplier. The information listed there is the only way to identify the flammability properties of a cable (horizontal, vertical, or bundle burning tests).
4. Which standards are typical for halogen-free cables?
Electrical cables must undergo testing to meet standards and be recognized as flame-retardant and halogen-free cables:
| Standard | Description | Test result |
| DIN EN 60754-1 VDE 0482-754-1:2021-02 | Defines the testing machines and the testing procedures required to identify the total acidity. | The test result must show values lower than 5mg/g to be certified as halogen free. |
| DIN EN 60754-2 VDE 0482-754-2:2021-02 | Defines the measurement of the pH value and conductivity. | The test result for the pH value must be below 4.3 and for conductivity, it must be under 10µS/mm. |
| DIN EN 61034-2 VDE 0482-1034-2:2021-02 | Defines the measurement of smoke gas density of burning cables. | The test result must show a light attenuation of no more than 40% to be considered low smoke. Depending on the application, customer, and region, lower light attenuation can be required. The goal is for people to be able to still recognise the source of the fire, as well as possible escape routes. These standards are required in public buildings and trains due to the high density of people present. |
In many applications where safety is critical, halogen-free cables and wires offer substantial advantages, as less toxic gas and smoke is emitted in the case of a fire. At the same time, these products must exhibit high flame retardancy in order to comply with different standards and requirements. It is not enough to rely on the common labels of FRNC, HFFR, LS0H, or LSZH to determine the actual flame retardancy of a cable. The standards named in data sheets are the only information you should rely on. It is through these standards that users can determine whether the product is considered to have low, middle, or high flame retardancy, if they are constructed to be low smoke, or if they have been tested for light attenuation. As experts for electrical connection technology with more than 45 years of experience, HELUKABEL is happy to help you identify the most ideal cables and wires for your application.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
Tel. +84 28 77755578 | info@helukabel.com.vn | www.helukabel.com.vn