Flame-retardant cables: How do they work and why do they matter?
Flame-retardant cables prevent the spread of fire during a fire event. Let’s go through the following article to discover the mechanism behind this.
Flame-retardant cables play a crucial role in ensuring safety across various applications, including residential buildings, industrial complexes, and manufacturing plants. These cables are engineered to resist the spread of fire, thereby safeguarding both property and human life. Understanding how flame-retardant cables function to prevent the spread of fire can assist in selecting the appropriate type of cable for different operating environments.
>>See more: HELUKABEL's flame-retardant cables
1. Overview of flame-retardant cables

Flame retardants are compounds added to the materials used in flame-retardant cables during or after manufacturing to prevent or slow down the combustion process. These substances act at various stages of the fire cycle, such as heating, decomposition, ignition, or flame propagation. Their primary function is to inhibit the spread of fire or to extend the time available for safe evacuation.
There are two types of flame retardants: additive and reactive. Additive flame retardants are incorporated into the plastic during the polymerization process, while reactive flame retardants are chemically bonded to the polymer's molecular structure. Reactive flame retardants are generally more durable because they remain integrated with the polymer, providing enhanced flame resistance throughout the material's lifespan.
2. Significance of flame-retardant cables

2.1 Flame-retardant cables support fire protection systems
Flame-retardant cables play a crucial role in supporting fire protection systems. These cables are designed to prevent or slow the spread of fire, providing additional time for firefighters to respond and ensuring a safer window for evacuation when necessary.
The flame retardants in these cables work by interrupting the combustion process through three key mechanisms:
- Inhibiting chain reactions: They disrupt the combustion process by capturing high-energy H and OH free radicals, which act as catalysts in the fire's propagation.
- Insulating fuel from heat: A protective layer, such as char or fire-resistant glass, forms on the cable's surface, preventing heat from directly reaching the underlying material and reducing the rate of thermal decomposition.
- Diluting combustible gases: Flame-retardant cables release water, nitrogen, or other inert gases, which lower the concentration of oxygen and flammable gases, effectively slowing the fire's development.

2.2 Flame-retardant cables adapt to evolving industrial landscapes
The driving force behind the rapid development of flame-retardant cables is the growing demand for safety across various sectors, many of which stringent performance and safety requirements are critical, particularly in industrial and manufacturing applications.
In today’s industrial landscape, with the advancement of materials science, traditional materials such as wood, metal, and animal fibers are being enhanced or replaced by new synthetic materials. While synthetic materials offer significant advantages such as reduced weight, increased durability, and lower production costs, new challenges related to fire resistance are also addressed. As a result, all materials used in industrial and manufacturing environments must adhere to the latest safety standards to ensure optimal performance and protection.
2.3 Ensuring compliance with fire safety standards
With increasing awareness of fire prevention in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, ensuring compliance with fire safety standards has become a top priority. Specific industries, such as steel, oil and gas, and chemicals, operate in harsh environments where the risks of fire and explosion are high. Consequently, these industries are required to comply with strict fire safety regulations, particularly regarding the selection and use of flame-retardant and fire-resistant cables.
Adhering to these regulations not only protects lives and property but also mitigates legal risks. Some commonly recognized standards for flame-retardant cables include:
- DIN EN 60754-1 VDE 0482-754-1:2021-02
- DIN EN 60754-2 VDE 0482-754-2:2021-02
- DIN EN 61034-2 VDE 0482-1034-2:2021-02
3. How do flame-retardant cables work?

Flame-retardant cables function through various mechanisms, depending on the type of flame retardant and the materials used.
3.1 Physical mechanisms of flame-retardant cables
Flame-retardant cables typically operate through three primary physical mechanisms to prevent or minimize the risk of fire and explosion. These mechanisms include:
- Cooling: Flame-retardant additives create an exothermic process that lowers the temperature of the material to below the combustion threshold. This is particularly critical in high-load cable systems where temperatures can rapidly increase.
- Creating a protective layer: A solid or gaseous barrier form around the flammable material, preventing oxygen from directly contacting the cable and inhibiting combustion. This protective layer also reduces heat transfer, ensuring the safety of both the cable system and associated electrical equipment.
- Dilution: Flame-retardant cables contain fillers that release inert gases during decomposition. These gases dilute the fuel in both solid and gas phases, reducing the fuel concentration below flammable limits and preventing ignition.
These mechanisms enhance the fire resistance of industrial cables, providing safety in complex manufacturing plants and industrial environments where high temperatures and fire risks are prevalent.
3.2 Chemical mechanisms of flame-retardant cables
Flame retardants typically interact with cable materials through chemical reactions that enhance the cable’s flame-retardant properties. These reactions alter the material, making it more resistant to ignition and flame propagation. There are two primary mechanisms of chemical reaction:
- Solid-phase reaction: In this mechanism, the flame-retardant forms a carbon layer on the surface of the material, usually the polymer layer of the cable. This process often involves dehydration, where the flame retardant removes water from the material and forms a carbon layer through cross-linking. This carbon layer acts as an insulating barrier, protecting the cable core by preventing high temperatures from further damaging the material.
- Gas-phase reaction: This mechanism disrupts the combustion process in the gas phase by neutralizing free radicals, which play a key role in sustaining flames. Breaking down free radicals halts heat release, lowering the material’s temperature. Additionally, it limits the supply of flammable gases, reducing the likelihood of fire.
4. Frequently asked questions about flame-retardant cables
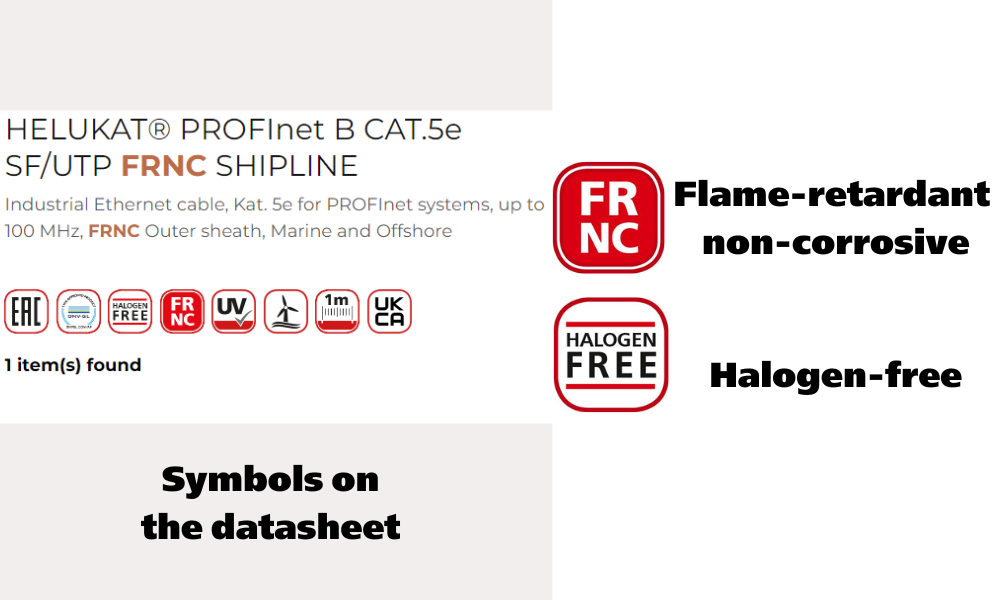
4.1 FRNC, HFFR, LSZH: what do these labels on flame-retardant cables mean?
While selecting flame-retardant cables, users will encounter various symbols such as FRNC (Flame-retardant non-corrosive), HFFR (Halogen-free flame-retardant), LSZH (Low smoke zero halogen) printed on the surface of the cables. All three indicate that the cables are flame-retardant and designed to minimize negative impacts during a fire. The primary difference lies in their protective features: FRNC focuses on preventing the release of corrosive substances, while HFFR and LSZH prioritize reducing toxic gases and smoke. However, to properly assess the effectiveness of flame-retardant cables, users should review the technical datasheets and consult experts for accurate guidance.
4.2 Are control cables flame-retardant?
Users have no difficulty in recognizing flame-retardant cables based on the labels listed above. Despite the absence of these symbols, many common types of cables such as control and signal cables are still flame-retardant. These cables still meet the required standards and undergo flame retardant testing. This information is clearly outlined in the technical datasheets for each product.
4.3 Are flame-retardant cables resistant to fire?
Flame-retardant cables are not fire-resistant completely but instead slow the spread of flames in the event of a fire. This helps to limit the rapid propagation of the fire, creating safer conditions for people and providing more time to respond to an emergency. However, flame-retardant cables cannot maintain their electrical performance during a fire, unlike fire-resistant cables. which are designed to continue conducting electricity for a certain period while being directly exposed to flames.
5. Common types of flame-retardant cables and applications

Flame-retardant non-corrosive cables (FRNC)
There are many different types of flame-retardant cables, some of which are indicated by cable symbols, making it easy for users to distinguish. However, there are also many types of cables with enhanced flame retardancy, which are not displayed on the cable explicitly.
5.1 Flame-retardant non-corrosive cables (FRNC)
Flame-retardant non-corrosive cables are designed to prevent the spread of fire while minimizing toxic smoke and corrosive gases in the event of a fire. Some of HELUKABEL's FRNC cables include:
- HELUKAT® PROFInet B CAT.5e SF/UTP FRNC SHIPLINE : This cable features a PP insulation core and a flame retardant, non-corrosive, halogen-free protective outer sheath. It also includes double shielding with plastic-coated aluminum foil (St) and a braided screen of tinned copper wire, making it especially suitable for marine and offshore applications.
- HELUKAT® 250S CAT.6 CMG SF/UTP PVC CHAIN : This cable also has double shielding and operates within a temperature range of -40°C to +80°C. It is specifically designed for applications in harsh environments, including use in drag chains.
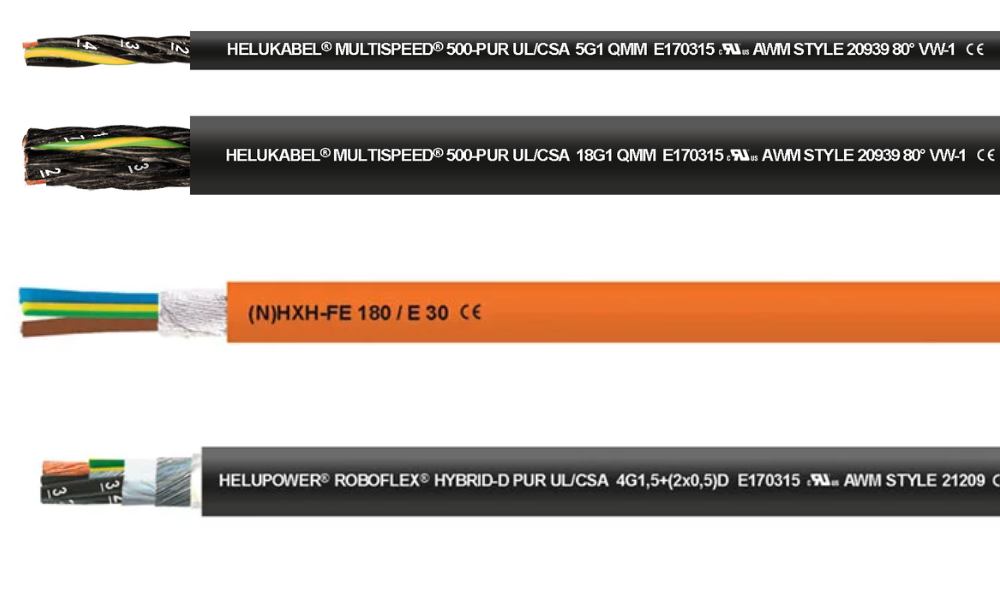
Halogen-free flame-retardant cables (HFFR)
5.2 Halogen-free flame-retardant cables (HFFR)
Some typical HFFR cables from HELUKABEL:
- MULTISPEED® 500-PUR UL/CSA : This cable features insulation made of special PP material, with an outer sheath made of special PUR material. It is flame-retardant and suitable for applications requiring high flexibility, abrasion resistance, and durability, such as cabling systems for industrial robots, production lines, automation systems, and continuously moving machine parts in multi-shift operations.
- (N)HXH-FE 180/E 30 : Designed for security systems, this cable offers enhanced fire protection properties and complies with DIN VDE 0266 standards. It is suitable for industrial areas, public spaces, buildings, mining sites, offshore structures, and more.
- HELUPOWER® ROBOFLEX® HYBRID-D PUR UL/CSA : This hybrid cable is designed to withstand both torsional and bending movements, making it ideal for applications requiring high mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and heat resistance. It is commonly used in robotic control devices, material handling systems, automation centers, transport systems, conveyors, turntables, and tilt tables, or anywhere that demands 3D movement and torsional loads, rather than just fixed direction bending.

5.3 Low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) cables
Some typical LSZH cables include:
- HELUPOWER® H07RN-F LS0H HAR cable is used as a power supply cable for solar power systems, can be used with voltages up to 1000 V AC or 750 V DC.
- HELUDATA® PLTC UL13 XLPE/LS0H IOS 300 is an instrumentation cable, used to transmit analog and digital signals in harsh environments such as the oil, gas and chemical industries.

5.4 Flame-retardant control and signal cables
Some control and signal cables with flame retardant properties have been tested and are designed for use in environments with high fire and explosion risks. Some typical flame-retardant control cables include:
- Y-CY-JZ / Y-CY-OZ : This is a line of anti-interference control cables with flame-retardant properties. It operates in a temperature range from -15°C to +80°C when flexing, and -40°C to +80°C in fixed installations.
- PAAR-TRONIC-Li-2YCYv : A twisted pair cable line designed to reduce crosstalk, making it particularly suitable for communication protocols like RS 422 and RS 485.
- RD-Y(St)Yv : These cables are used in measurement and control technology, as well as in industrial plant control stations. They transmit analog and digital signals with frequencies up to 10 kHz and are suitable for fixed installation indoors, outdoors, and underground.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |