Differences between rubber cables and PVC cables
Rubber cables and PVC cables are both widely used in industrial applications. So, what are the differences between these two types of cables? Let’s explore through the following article!
Rubber cables and PVC cables are two common types of electrical cables widely used in various fields. Although both serve similar functions, they differ significantly in several aspects. In this article, we will introduce the differences between PVC cables and rubber cables to better understand their respective advantages, limitations, and suitability for diverse applications.
1. Overview of rubber cables

Rubber cables are also commonly used in marine and offshore applications
1.1 What are rubber cables?
Rubber cables are a type of electrical cable with insulation and/or outer sheath made from rubber, providing flexibility, high durability, and good resistance to various environments. Known for their flexibility, rubber cables are used in many settings due to their resistance to water, oil, and abrasion.
In industrial landscapes, this type of cable supplies power to mechanical equipment that requires wiring systems capable of withstanding strong vibrations, serving as a flexible connection for mobile devices. Rubber cables are also commonly used in marine and offshore applications, such as powering submersible pumps, thanks to their superior water resistance. Under harsh conditions, such as high temperatures or exposure to chemicals, rubber cables are preferred for ensuring integrity. Moreover, this type of cable is widely used in residential and commercial applications.
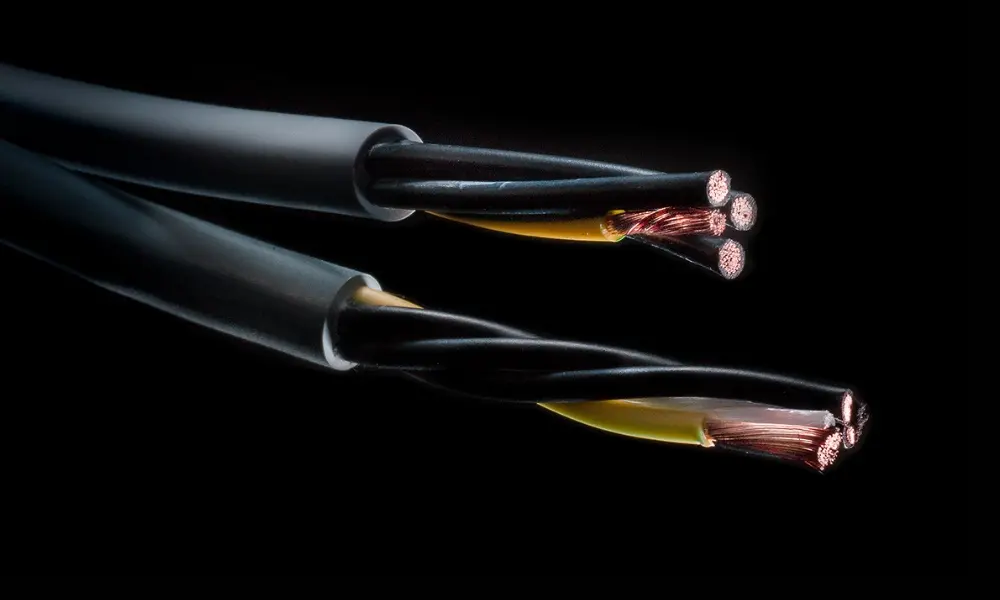

1.2 The structure of rubber cables
The structure of rubber cables typically consists of three main components:
- Conductor: Similar to other cables, the conductor of rubber cables is usually made from copper or aluminum, with the strands braided together to enhance flexibility and ensure good electrical conductivity. Copper conductors are often preferred due to their superior conductivity and higher temperature resistance compared to aluminum.
- Insulation: The insulation layer of rubber cables is made from materials such as natural or synthetic rubber (e.g., EPDM, EPR, NBR). This insulation not only provides electrical separation between the conductors but also enhances thermal resistance and protects against environmental impacts.
- Outer sheath: The outer sheath of rubber cables is commonly made from synthetic rubber, such as chloroprene (CR) or silicone rubber. This sheath protects the cable from mechanical impacts, abrasion, chemicals, oils, and harsh weather conditions. The sheath also allows the cable to withstand continuous bending, which is crucial in moving applications.
2. Comparing rubber cables and PVC cables
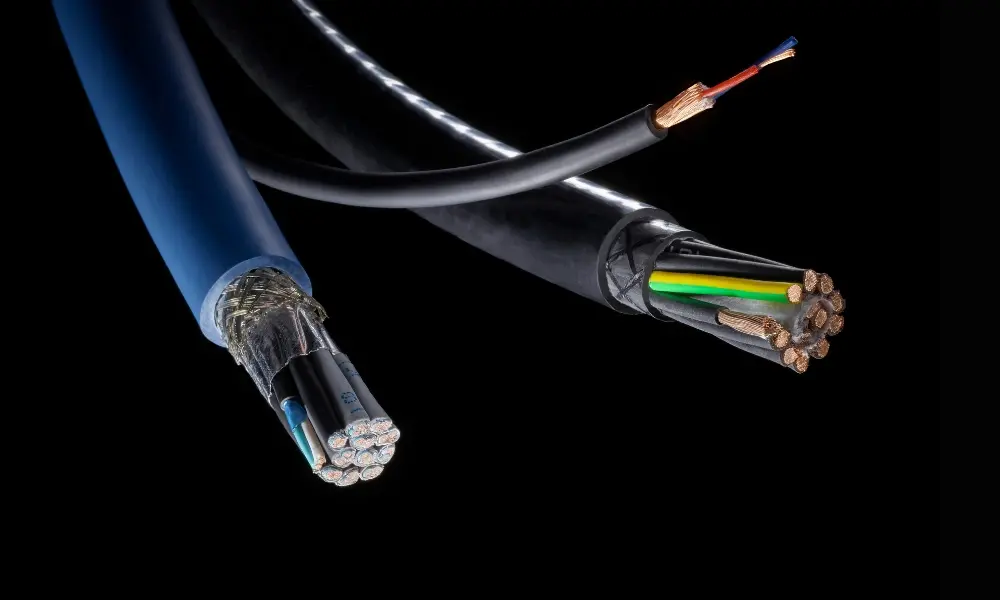

PVC cables are made from Polyvinyl Chloride, a thermoplastic synthetic material
2.1 Material
PVC cables are made from Polyvinyl Chloride, a thermoplastic synthetic material known for its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PVC is created through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers, resulting in a material that is both rigid and flexible, making it suitable for insulation and sheathing for cables. Various additives are often incorporated into PVC cables to enhance properties such as fire resistance, UV resistance, and increased flexibility.
In contrast, rubber cables utilize rubber as the primary material for insulation and sheathing. Rubber can be sourced from natural or synthetic origins, with synthetic rubber variants providing better performance and higher consistency. The flexibility and resilience of rubber make it ideal for applications that require the cable to bend, twist, and move frequently.
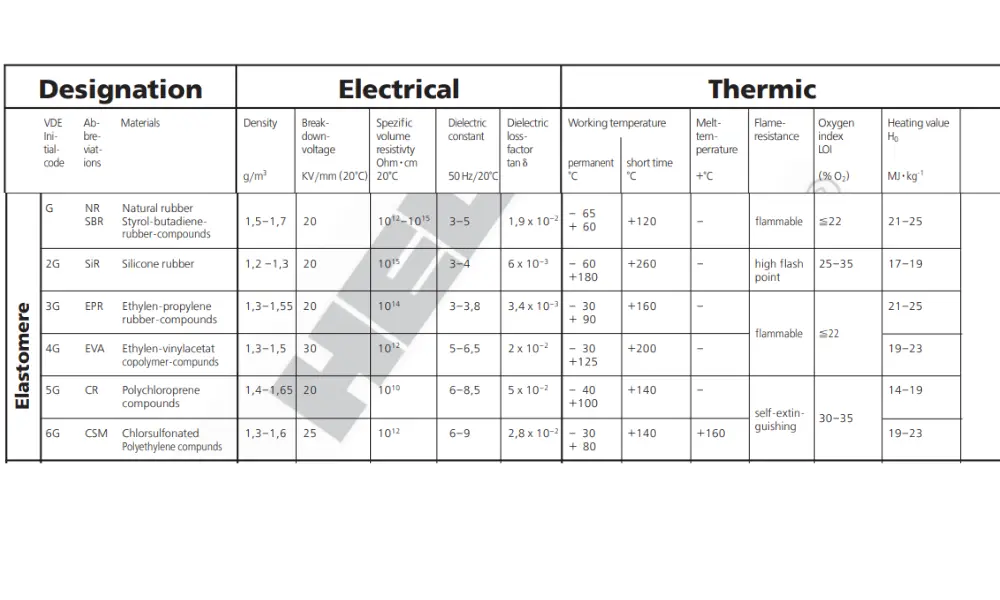
Electrical properties of some rubber cables
2.2 Rubber cables exhibit better electrical properties
Rubber cables generally possess better electrical properties compared to PVC cables. Rubber has higher dielectric strength and can withstand higher voltage levels, making it a suitable choice for high-voltage systems. PVC cables, on the other hand, are more suitable for low-voltage applications.
Moreover, silicone rubber cables offer high insulation resistance, which helps minimize the risk of short circuits or electrical leakage. This property is particularly crucial in industries where safety is a top priority, such as medical equipment, power generation, or hazardous environments.
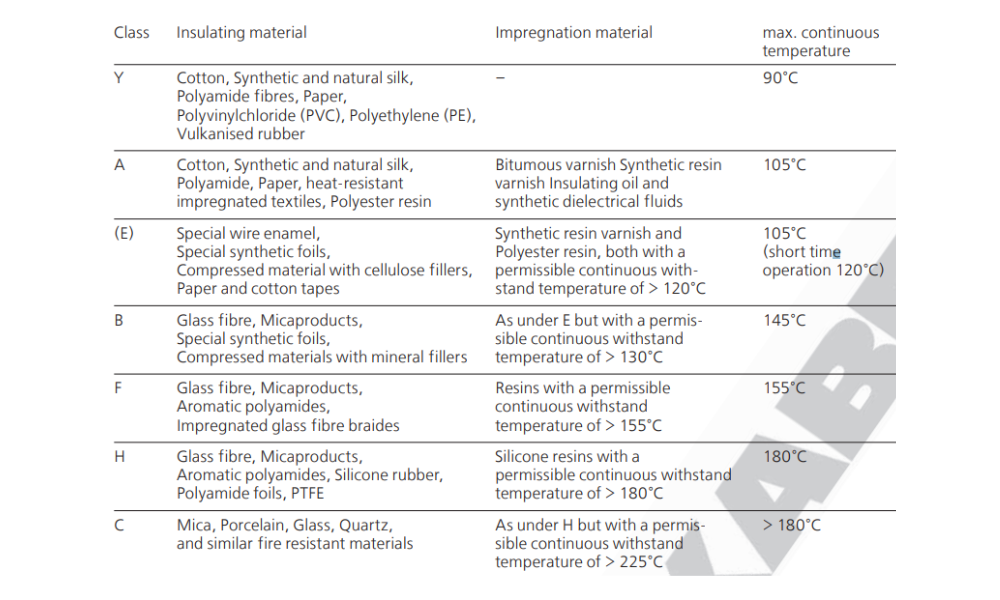
Temperature-resistant capabilities of rubber cables
2.3 The flexibility of rubber cables and PVC cables
PVC cables have moderate flexibility compared to rubber cables. The natural properties of rubber allow cables to bend and twist easily without compromising their structural integrity. This flexibility makes rubber cables an ideal choice for applications that require frequent movement, vibration, or bending of the cables.
2.4 Temperature-resistant capabilities
PVC cables have limitations when it comes to temperature range compared to rubber cables. While PVC can withstand moderate temperatures, at very low temperatures, it becomes brittle, and at high temperatures, it softens. Extreme temperature variations can affect the flexibility and mechanical properties of PVC cables, potentially leading to cracking or deformation over time.
Rubber cables, on the other hand, can endure a wider temperature range, including extreme heat and cold, without compromising flexibility or performance. This heat resistance makes rubber cables well-suited for outdoor applications where exposure to harsh environmental conditions is frequent.
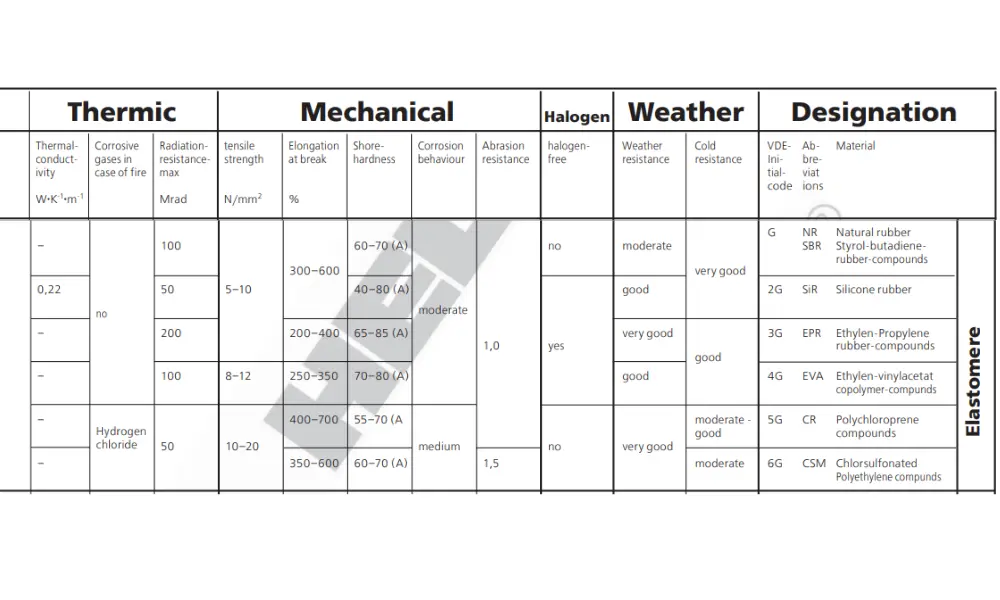
Environmental resistance of rubber cables
2.5 Environmental resistance
PVC cables offer good resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor installations with moderate environmental exposure. However, PVC may degrade over time when exposed to certain chemicals or oils, limiting its use in environments that require high chemical resistance. In contrast, rubber cables exhibit superior resistance to moisture, oil, chemicals, and abrasion, making them ideal for harsh environments such as industrial zones, construction sites, and outdoor installations. The natural elasticity of rubber allows the cable to maintain performance and integrity even under the most extreme conditions.
2.6 Rubber cables are generally more expensive
PVC cables typically have a lower cost, providing a balance between performance and cost, which makes them widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. In contrast, rubber cables are usually more expensive due to the higher cost of rubber and the additional manufacturing processes required to produce flexible rubber insulation.
In summary, the choice between PVC and rubber cables will depend on the specific requirements of the electrical system and the environment in which the cables will be used. Rubber cables are often more suitable for harsh environments and high-voltage systems, while PVC cables are a more cost-effective option for low-voltage applications.
| Rubber cables | PVC cables | |
| Insulation/Outer sheath | Rubber | PVC |
| Electrical properties | Good, suitable for high voltage applications | Suitable for low voltage applications |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Temperature resistance | High | Medium |
| Environmental resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | High | Low |
3. Applications of rubber cables

Rubber cables can be used in a variety of applications, both indoors and outdoors. Some common applications of rubber cables include:
- Industrial environment: Rubber cables are often utilized in industrial settings such as factories, power plants, and other manufacturing environments to transmit electrical power and signals. This type of cable is resistant to oil, water, and other substances, making it suitable for use in harsh conditions.
- Outdoor environments and heavy-duty industries: Rubber cables are frequently used in outdoor environments, including construction, mining, and other industrial applications. They offer excellent abrasion resistance and can withstand mechanical stress, making them a durable choice for outdoor applications.
- Marine and offshore applications: Rubber cables are commonly employed in marine and offshore applications due to their resistance to saltwater and other corrosive substances.
- Residential and commercial environments: Rubber cables can also be used in residential and commercial settings, such as for electrical installations for appliances, lighting systems, and other electrical devices.
4. Common types of rubber cables
4.1 Heat-resistant rubber cables
Rubber cables designed for high-temperature resistance are used in environments with elevated temperatures, particularly in the metallurgy and steel industries. Some notable products from HELUKABEL include:
- SiHF: This is a cable series with insulation and outer sheath made from silicone, operating in a temperature range from -60 °C to 180 °C. In terms of properties, this cable series is resistant to ozone, oxygen, dilute acids, alkalis, salt solutions, oxidizing agents, high molecular weight oils, vegetable and animal fats, plasticizers, chlorophenols, and seawater. Consequently, this cable series is utilized in steel production, shipbuilding, as well as in factories producing ceramics, glass, and cement.
- SiHF-C-Si: This is a silicone rubber cable with enhanced heat resistance, EMC-preferred type. Its halogen-free nature makes it highly suitable for applications in the iron and steel production industry, rolling mills, foundries, aircraft construction, and shipbuilding, as well as in factories producing cement, glass, and ceramics. This rubber cable also demonstrates effective applicability in high-power lighting fixtures, as well as all types of heating equipment.
- THERMFLEX® 180 EWKF: This cable offers higher mechanical strength, better abrasion resistance, and a longer lifespan compared to standard silicone cables, thanks to its EWKF quality (EWKF stands for Einreiß-, Weiterreiß- and KerbFestigkeit, meaning tear, tear propagation and notch resistance).
4.2 Oil-resistant rubber cables
Oil-resistant rubber cables are used in oil and grease-rich environments, such as in oil and gas facilities or the chemical industry.
- H07RN-F / 07RN-F: These cables are oil-resistant and weather-resistant, making them suitable for heavy industrial applications. Known for their high durability, this rubber cable series is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings that require medium to high mechanical stress, such as agricultural electrification, port machinery, drainage stations, and irrigation systems.
- NSHTÖU: This cable is designed for reeling applications with high mechanical stress, with a maximum acceleration of 0.4 m/s² and a maximum speed of 120 m/min. Common applications include construction machinery, conveyor belts, and cranes.
- NSSHÖU: Featuring an insulation layer made from a plastic-rubber composite (EPR), this cable improves ozone resistance. It is used as a connection cable for applications with very high mechanical stress in mining, surface mining, and construction sites. However, the NSSHÖU cable is not suitable for drumming or continuous movement applications, such as robots.
4.3 Water-resistant rubber cables
This rubber cable is ideal for outdoor use or in areas with high humidity.
- HELUPOWER® H07RN-F LS0H: This rubber cable is suitable for outdoor applications and can be used in stagnant water (including saltwater) at a maximum depth of 100 meters (AD8), with a minimum water temperature of +5°C.
- HELUPOWER® SOOW and HELUPOWER® SJOOW: Both cables feature an insulation layer made of EPR rubber, and an outer sheath made of CPE rubber. They exhibit excellent resistance to oil, ozone, grease, water, and UV radiation. These cable types are commonly used as power supply cables in factories and processing facilities, cranes, lifting equipment, construction machinery, and motors.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |