What are cable connectors? Functions and applications of cable connectors
Cable connectors play a crucial role in transmitting signals and power between electrical systems across various industries. Depending on specific applications, there are specialized types of cable connectors. Let's explore what cable connectors are and discover the most common types through the following article.
1. What are connectors?
An electrical connector is an electromechanical component that provides a detachable interface between two parts of an electrical system without compromising system performance. This detachable nature allows separately manufactured circuits to be easily connected, tested, maintained, and upgraded. These subsystems (component assemblies) can be inspected and upgraded independently. Cable connectors solve issues related to fixed connections between components and eliminate problems that arise from rewiring, such as damage to conductive pathways on circuit boards caused by repeated soldering and desoldering.
Depending on the application field and transmission quality requirements, cable connectors are designed to meet specific purposes or applications - taking into account technical conditions, commercial demands, technological advancements, environmental and economic factors, increasing data transmission speeds, and the demand for higher performance and reliability. To meet these requirements, cable connectors are made in various standards, shapes, sizes, and configurations. Each type of connector is customized to fit specific applications and industries.
2. Functions of cable connectors

Cable connectors establish electrical, mechanical, or optical connections between electrical, electronic, or mechanical components, allowing continuous flow of current, signals, or data. Some of the main functions of electrical connectors include:
- Data transmission: One of the basic functions of an electrical connector is to support data transmission between devices. Connectors ensure smooth and fast data transfer, whether it's transferring files between a computer and a USB drive or streaming high-quality video from a player to a TV via an HDMI cable.
- Signal integrity: High-quality cable connectors are essential for maintaining signal integrity during data transmission. A well-designed connector minimizes signal loss and interference, resulting in higher performance and reliability.
- Power supply: Power connectors are responsible for supplying electricity to various compatible devices, from small electronic gadgets to heavy industrial machinery. These connectors can handle specific electrical requirements and ensure safe power delivery.
- Audio and video transmission: Audio and video connectors are crucial for transmitting high-quality audio and video signals between devices like speakers, headphones, TVs, and projectors, ensuring accurate audio and visual content reproduction.
- Network and internet connectivity: Ethernet connectors, commonly found in networking devices, enable devices to connect to local networks and the Internet. They play a key role in providing internet access and local data sharing.
- Mechanical fixation: Connectors often provide mechanical fixation, helping to secure components while maintaining electrical connectivity. This is especially important in industrial and automotive applications where there is significant vibration and movement.
3. Key components of cable connectors
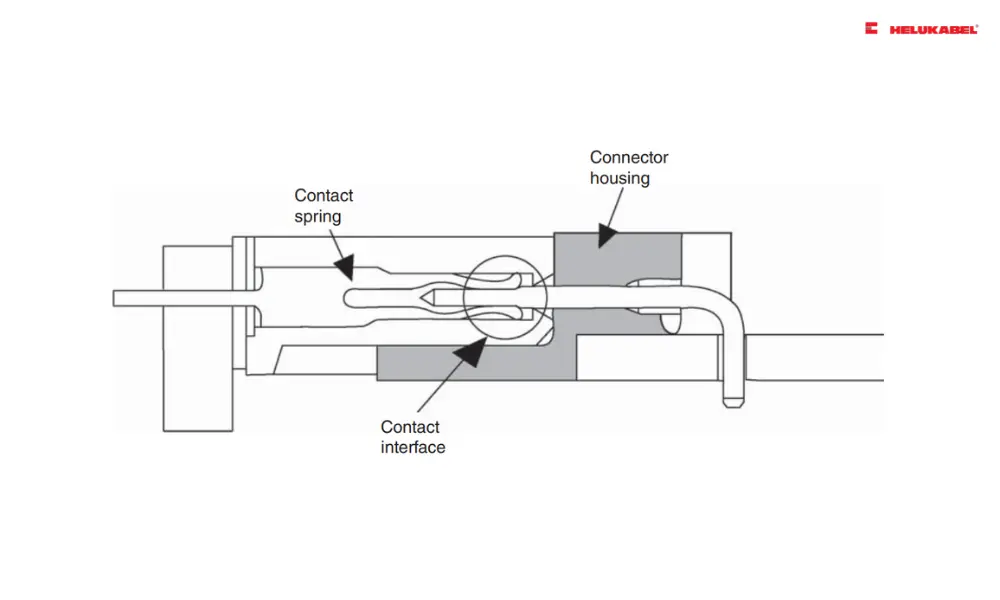
Main components of cable connectors. Source: Pecht, M., & Kyeong, S. (2020). What Is an Electrical Connector?. Electrical Connectors: Design, Manufacture, Test, and Selection, 1-15.
The main components of cable connectors include contact springs, contact finishes, and contact housing. The contact interface is defined by the physical-electrical connection between the mated parts of the connector, which determines the performance of the electrical connectors.
3.1 Contact springs
The contact spring creates the pathway for transmitting signals, power, and/or grounding between the circuits that the connector links. This component also provides perpendicular pressure on the contact surface, forming and maintaining a separable interface. Key mechanical requirements for the contact spring include insertion and extraction force, contact force, contact retention, and contact wipe. Electrically, the contact spring must meet criteria such as contact resistance, rated current, inductance, capacitance, and bandwidth.
There are two types of contact springs: the receptable, usually the flexible component, and the plug, which is typically rigid and helps deflect the receptable spring to create contact pressure. The receptable spring ensures low insertion force when mating and allows the electrical connector to withstand misalignment stress during insertion.
3.2 Contact finishes
The contact finishes protect the base metal of the contact spring from corrosion and minimizes the formation of films on the contact spring’s surface. For optimal effectiveness, the contact finish should completely cover the contact spring and be resistant to corrosion.
Films that can increase contact resistance include thin oxide, sulfides, chlorides, and complex mixtures of metal films forming on the contact surface. To reduce contact resistance, a film-free metal surface is needed. The type of finish determines the type of surface film that may form on the contact interfaces. Precious metals, especially gold, are inert as they do not form oxide layers on the surface. In contrast, with non-precious metal finishes such as tin, tin oxide may form on the contact spring, which may require periodic removal.

Most contact housing designs are similar, but the materials used can vary
3.3 Contact housing
Electrical cable connectors must maintain dimensional stability under the impact of harsh chemical and temperature conditions. To ensure proper assembly and operation, the connector's center line spacing, straightness, and flatness must be maintained. The connector housing achieves this stability by providing insulation and mechanical protection for the contact spring, securing the position of contacts, and shielding them from environmental conditions.
Most contact housing designs are similar, but the materials used can vary. These materials not only meet environmental operating conditions but also withstand production and assembly processes. Common materials used for connector housings include polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), PCT, liquid crystal polymer (LCP), FR-4, and polyimide.
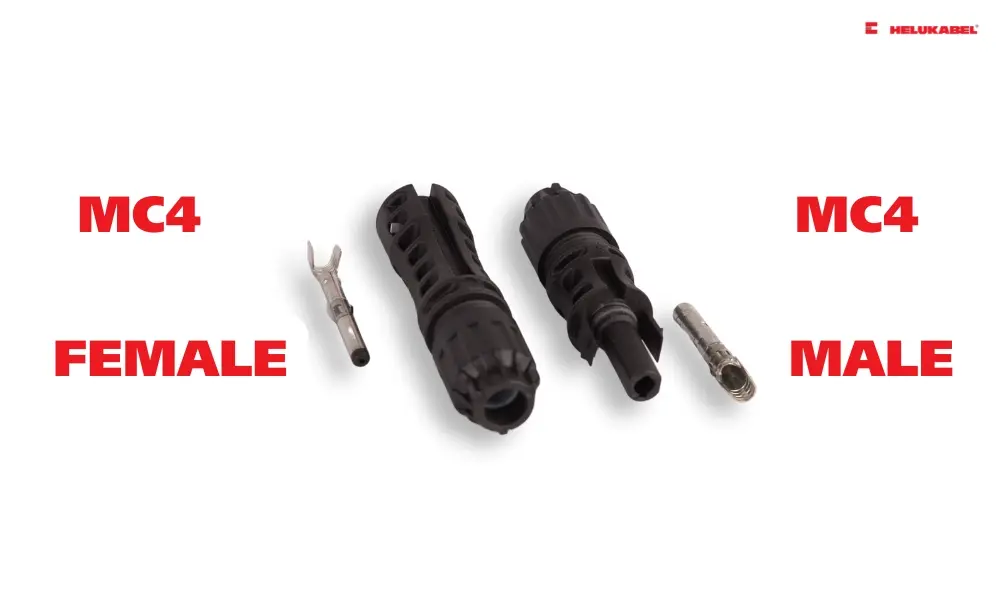

Male vs female DC cable connectors
3.4 Contact interface
When male and female cable connectors make contact, a separable interface is established. To achieve the desired electrical performance, it is essential to create and maintain contact interfaces. This metallic interface is formed mechanically.
When separable connectors are mated, only the highest points on the surface, known as "asperities," come into contact with each other. Therefore, the entire surface of the cable connector does not fully touch. The asperities depend on the shape of the contact surfaces. The size and number of these asperities depend on the surface roughness and the applied load. This load also determines the extent of the contact area.
4. Applications of cable connectors
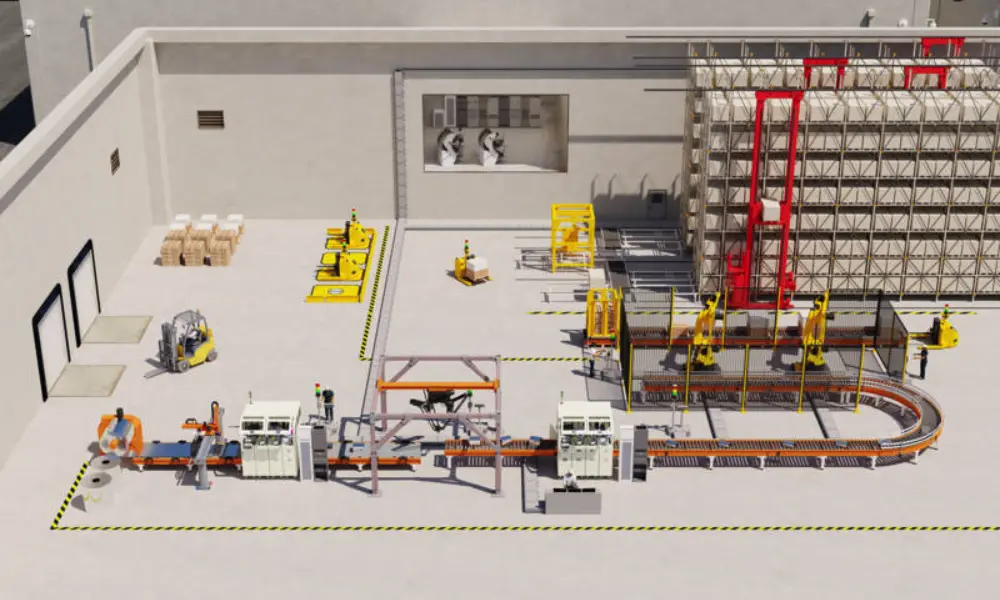
4.1 Industrial electronics and automation
Industrial electronics is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the industry. Characterized by automation technology, industrial electronics encompasses a wide range of fields, from process and production engineering, building and residential automation, power generation and distribution, and transportation (transport technology, railways, aviation, and marine) to medical engineering and professional entertainment systems.
Automation devices and components, such as controllers, I/O elements, and inverters within control cabinets, are typically equipped with specialized cable connectors. These connectors maximize flexibility in connecting sensors and actuators inside the cabinet, as well as in supplying power between components and from components to the external environment.
4.2 Building automation
Due to installation conditions, field-assembly cable connectors are primarily used in building automation, especially plug-type connectors. The cable cores are connected directly to the cable connector on-site by the installer. Screw clamps, widely used in the past, are gradually being replaced by spring clamp contacts. Insulation displacement connection (IDC) technology is also employed in certain areas.
Given the long lifespan of buildings and some safety-critical applications (such as fire prevention or access control), connectors used in building automation must be highly reliable and durable. They need to handle both the transmission of low signals from sensors (such as temperature, brightness, occupancy, or air quality sensors) and higher currents for actuators (like control motors, fans, or lights).
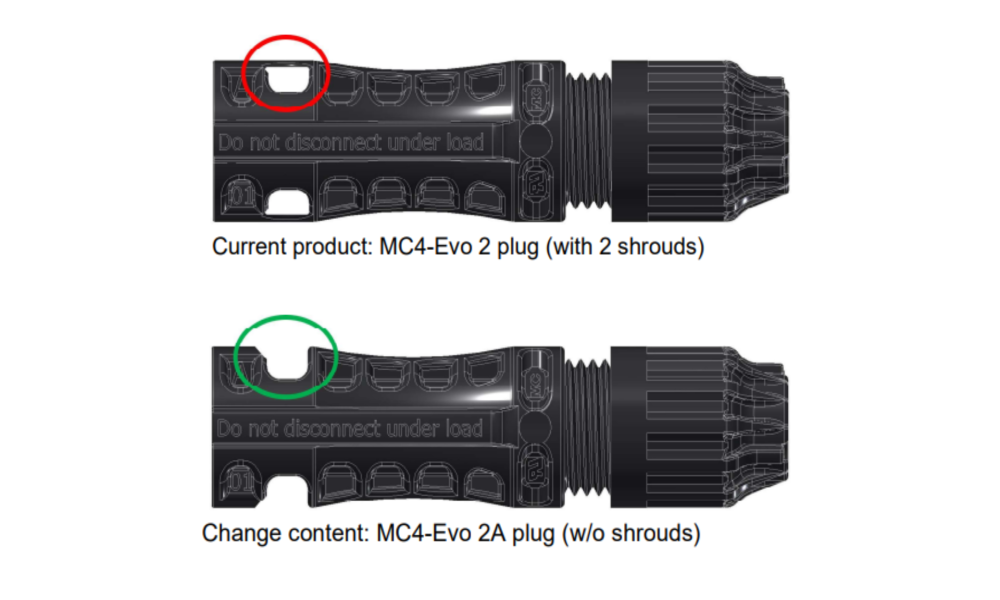
MC4-Evo 2 and MC4-Evo 2A connectors for photovoltaic systems
4.3 DC connectors for photovoltaic systems
DC cable connectors are essential components in photovoltaic systems, ranging from large solar farms to rooftop modules for households. Thanks to DC cable connectors, technicians can quickly install PV modules and converters in the field without needing special tools.
DC cable connectors are designed to be compatible with solar cables, accommodating conductor cross-sections from 2.5 to 16mm², and supporting current transmission up to 65 A. They can handle higher direct current (DC) voltages, up to 1500 V, and meet IP68 standards for water and dust resistance, ensuring durability in various environmental conditions.
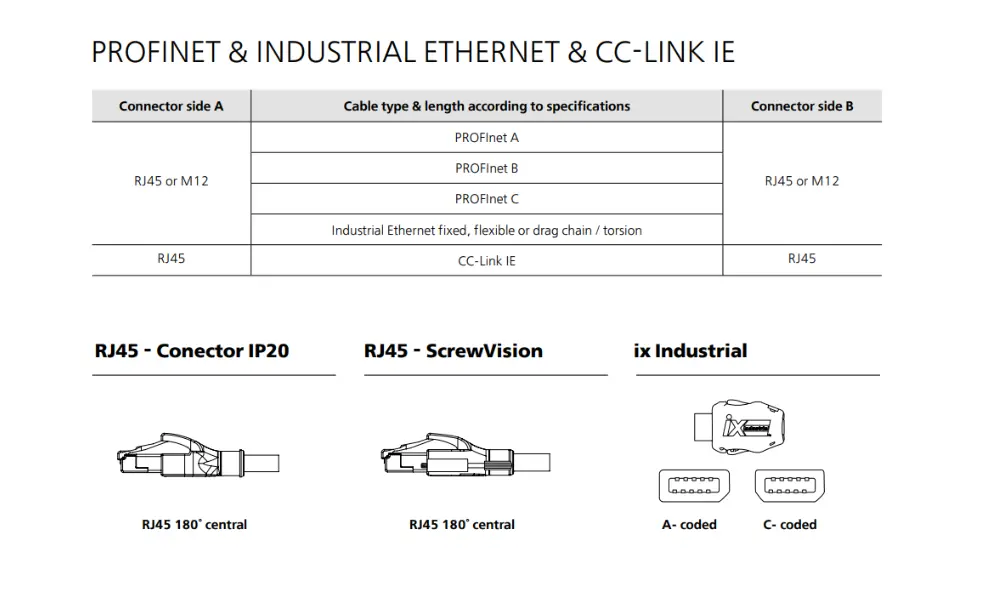
Some cable connectors for telecommunications
4.4 Telecommunications
Communication is the foundation of today’s technological trends. Concepts like the "Internet of Things" (IoT), "Industry 4.0," and "Mobility" all rely on high-performance communication links and extensive data accessibility. Electrical cable connectors play a crucial role in building these networks, supporting maintenance and adaptation needs as data transmission speeds increase. The widespread use of these systems demands a high degree of connector standardization. For instance, connectors such as RJ45 or USB have become some of the most widely used components globally.
Electrical cable connectors are key components in systems like:
- Data centers and switching technology
- Mobile devices
- Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN)
4.5 Connectors for automative
Connectors in automotive electronic systems must withstand harsh conditions such as strong vibrations, high temperatures, humidity, and chemical exposure. These cable connectors support critical systems, including drivetrain control, safety control systems (e.g., ABS brakes, airbags), infotainment systems, and advanced sensors like backup cameras and driver assistance radars.
Automotive electronic connectors are typically compact, designed with secure locking mechanisms to prevent accidental disconnections, and equipped with electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding to maintain signal accuracy. Additionally, hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) are subject to even higher temperatures and significantly greater vibration forces than conventional vehicles, creating more stringent requirements for connector design, base materials, and contact surfaces.
Connectors in EVs must be constructed from heat-resistant materials with high mechanical durability and wear resistance to ensure stable connections in extreme operating environments. Common standards for EV charging connectors include types like Type 1 and Type 2, which are widely used for different regions and charging applications.
If you still have any concerns or questions about cable connectors, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |