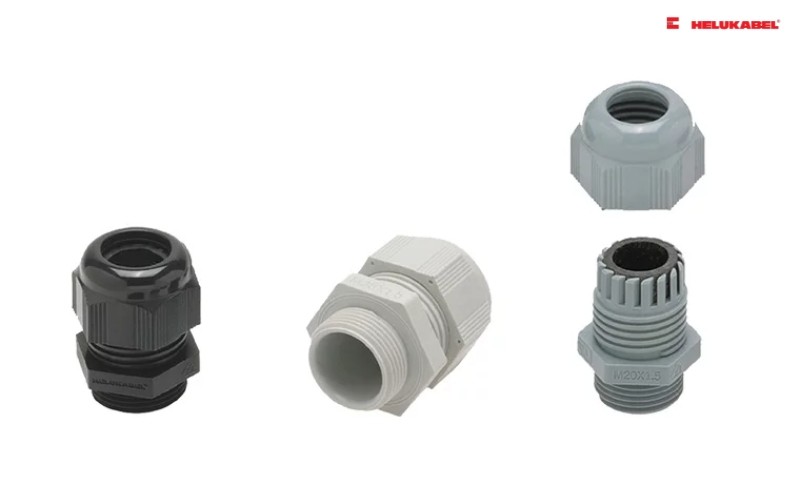
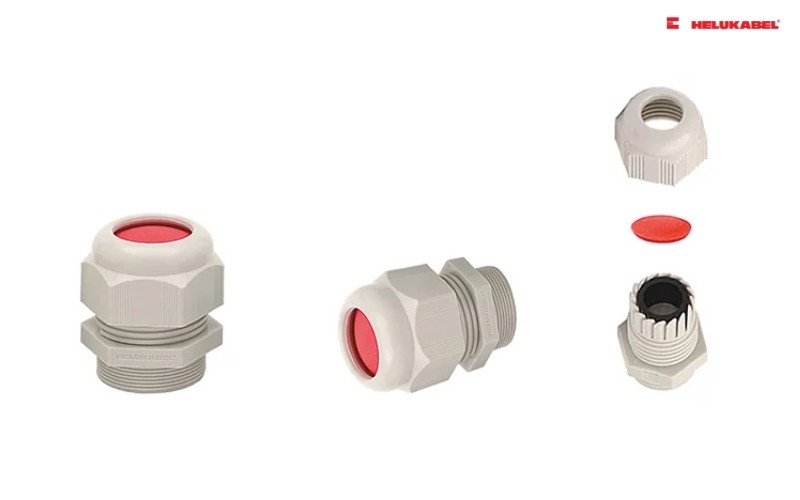
What are cable glands? Why are they used?
Cable glands protect both the cable and the interior of the enclosure from mechanical stress and external influences. Let’s explore key information about cable glands in this article!
1. What are cable glands?
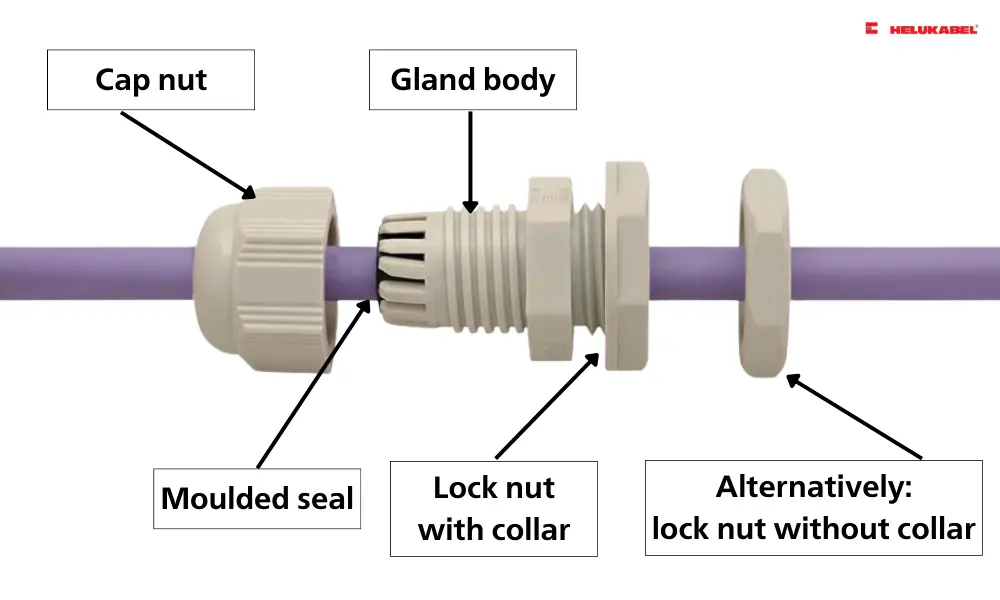
Structure of plastic cable glands
Cable glands are an essential component of the cabling process, especially in plant engineering and control cabinet construction. A cable gland is a small device used wherever electrical cables need to pass through control panels, junction boxes, electrical cabinets, automation systems, measuring tools, and control devices. Cable glands provide a safe and tight connection between the cable and the housing wall, preventing the intrusion of dust, moisture, and other external factors. Depending on their specific design, cable glands can also perform functions such as grounding, preventing bending and twisting, or reducing tension on the cable.
The European standard EN 62444 specifies metric threads for cable glands, ranging from 6 to 110 mm. Additionally, PG cable glands have steel conduit threads, and in the US, self-sealing NPT threads are also used. Cable glands are typically made from materials such as brass, stainless steel, or polyamide plastic, depending on application requirements. For example, copper cable glands can prevent electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues, while stainless steel versions are popular in applications that require durability and hygiene, such as food production.
>>See more: A glance at cable glands' applications
2. Why are cable glands used?
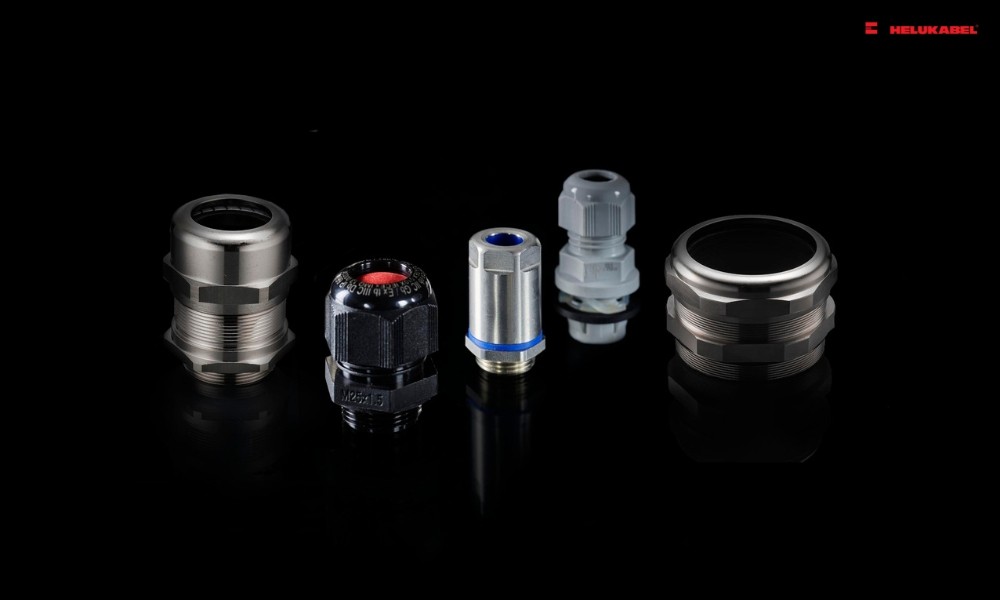

Cable glands serve the following functions:
2.1 Cable protection
Cable glands can be sealed on the housing to prevent dust and moisture from entering the electrical or tool housing. They can also protect sensitive wiring from contamination, corrosion, and flammable gases.
2.2 Strain relief
A wire always moves to a greater or lesser extent – both during installation, and in long-term use. It is important to protect it against tensile loads. The movements may be either constant or intermittent. For this reason, a cable gland with strain relief is necessary. Strain reliefs are described in EN 50262. Generally, cable glands have strain relief A.
2.3 Sealing with insert
A seal is compressed by tightening the cap nuts. When the cap nuts are screwed tight, lamellae press against the moulded seal – the wire is thereby sealed, and the strain is relieved. The advantage of the clamping lamellae is that they make a large clamping range possible, to allow for different wire diameters.
2.4 Resistant to environmental conditions
Different applications demand different levels of resistance. Plastic cable glands made from polyamide can be used at temperatures from -30 °C to +80 °C. They are resistant to abrasion and impact as well as hydrocarbon/fuels and cleaning agents. In contrast, stainless steel cable glands are highly compatible with heavy-duty industries – they are waterproof and resistant to many disinfectants used in food production.
2.5 Compact design
Cable glands are designed to eliminate the need to disassemble each internal component during the assembly process. When adjustment is needed, users only need to loosen the nut, simplifying maintenance and saving time.
3. Cable glands classification
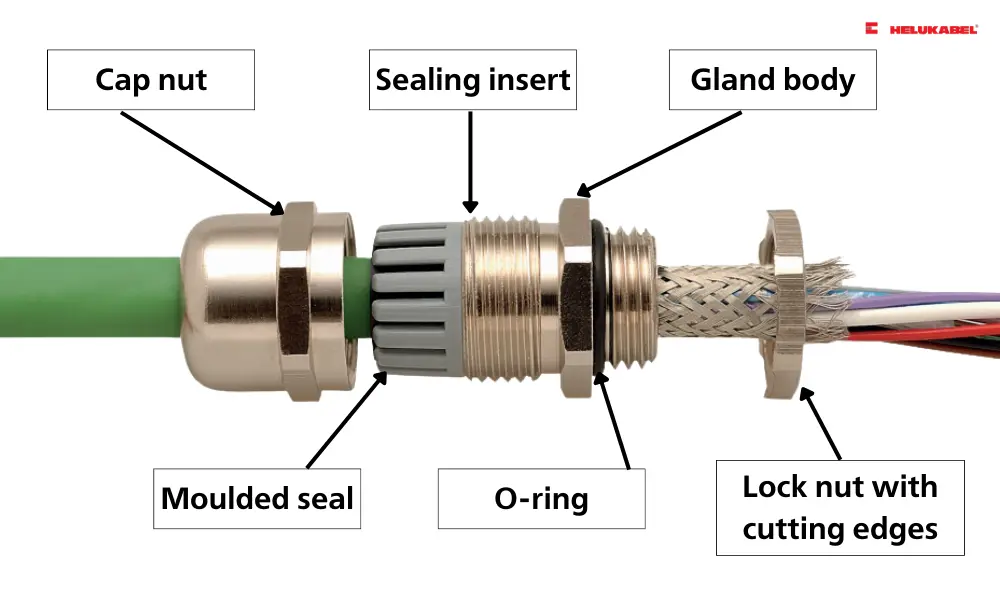
3.1 Metal cable glands
Metal cable glands are made from materials such as stainless steel, nickel-plated brass or aluminum. These materials are the most stable and durable options when a strong connection is required. Metal cable glands can conduct heat and resist corrosion, making them the ideal choice for connecting medical and chemical equipment, information technology equipment, and electrical equipment.
>>See more: Stainless steel cable glands
3.2 Plastic cable glands
Plastic cable glands offer stable, flexible, and cost-saving solutions for applications that are not exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Most plastic cable glands are made from polyamide or nylon, capable of corrosion resistant. Thus, plastic materials are opted for when connecting cables to equipment in telecommunications and maritime applications, as well as equipment that uses flex cables.
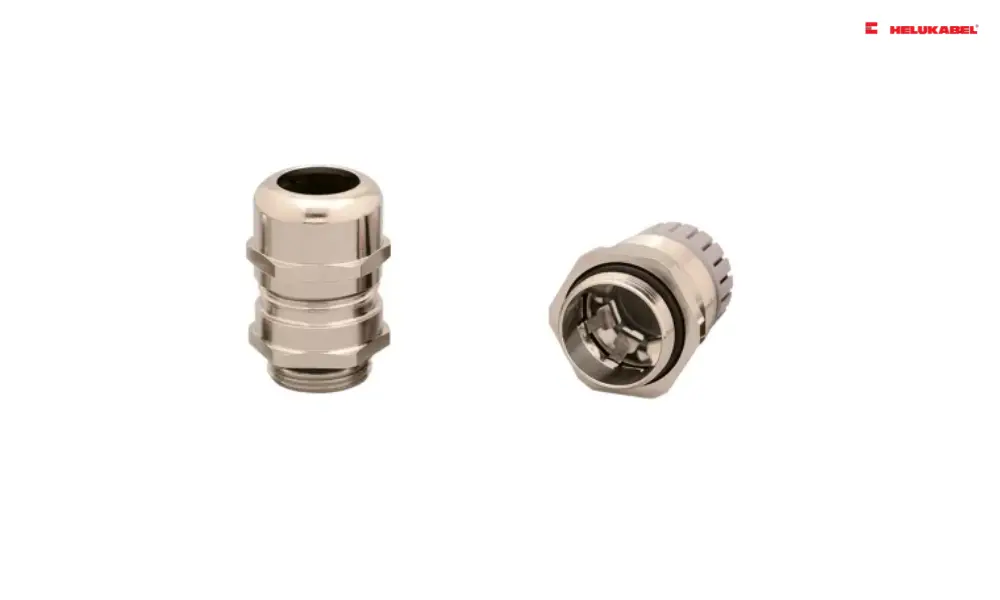

HELUTOP® MS-EP4 cable gland
3.3 EMC cable glands
EMC cable glands protect cables and equipment from EMI that affects the function of electrical equipment. Using EMC cable glands creates a barrier against EMI at the termination point. EMC cable glands are prevalent in telecommunications applications and other similar cases where EMI are detrimental to the machine.
3.4 Threadless cable glands
Threadless cable glands avoid the conventional connection techniques of threaded holes or locknuts. Instead, they feature a spring-loaded, snap-in system that simply needs to be pushed into the panel or enclosure opening for installation. The fitting can then be locked in place by tightening the gland clockwise. No installation tools are required, and hand tightening alone provides the same level of anti-rotation protection as nut or tapped hole versions. This simple technique allows threadless cable glands to be fitted into hard-to-reach areas or where space is limited.
4. HELUKABEL’s cable glands
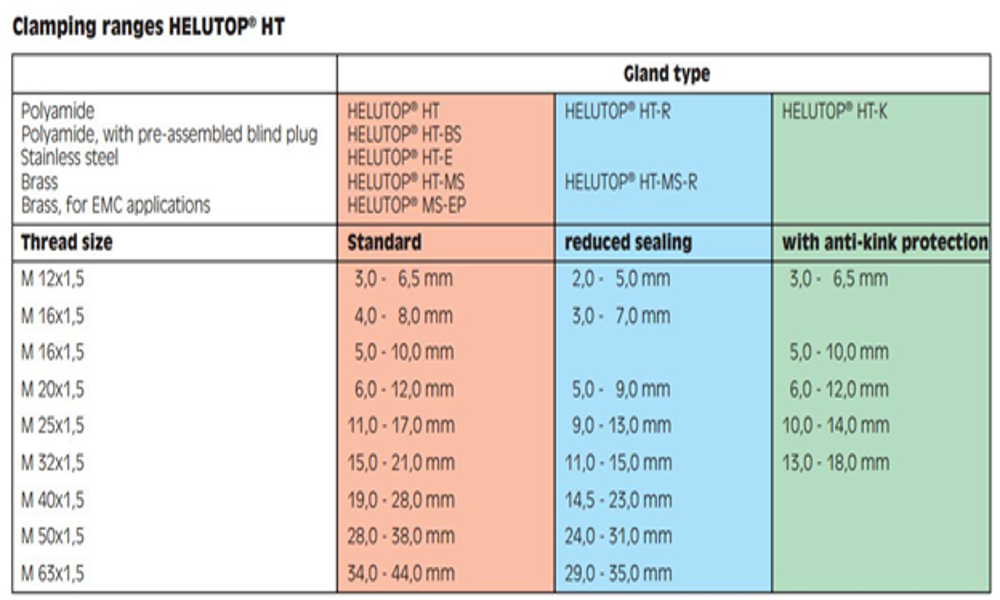
4.1 HELUKABEL’s plastic cable glands
The cap nut and gland body are made of polyamide PA6 in the following colors: light grey RAL 7035, dark grey RAL 7001, black RAL 9005. Polyamide PA6 is abrasion- and impact resistant, and resistant against hydrocarbons/fuels and cleaning agents. It is tried-and-tested as a material for cable glands in standard applications. The moulded seal is made from neoprene. The cable glands HELUTOP® HT are fitted with vibration protection for secure attachment in mobile applications. The lock nuts with or without collar are made from polyamide PA6.
Compatible accessories for plastic cable glands include lock nuts, adapters, enlargers, reducers.
HELUTOP® HT plastic cable glands from HELUKABEL adhere to VDE standard, are free from phosphor, silicone, cadmium, optimum strain relief through clamping plates. Therefore, this type of cable glands is used in manifold industries such as automation, robotics, installation technology, control cabinet construction…
HELUTOP® HT plastic cable glands are also available in many variants with enhanced features such as HELUTOP® HT-BS with dust protection, HELUTOP® HT-K with anti-kink spiral capabilities for mobile use.
4.2 Stainless steel cable glands
HELUKABEL’s stainless steel cable glands exhibit the following characteristics:
Cap nut and gland body are made from stainless steel. Due to their high degree of corrosion resistance and longevity, these glands are suitable for tough conditions: Heavy chemical loads, cleaning agents (e.g. in the food industry), weather-resistant when used outdoors.
The terminal insert is made from polyamide PA6.
The moulded seal is made from neoprene.
The O-ring is made from Buna-N.
The lock nuts are made from stainless steel.
HELUTOP® HT-Clean steel cable glands meet VDE standards and the highest standards for dust and splash resistance, so they are used in many industries with harsh environments such as the F&B industry, the pharmaceutical industry, biotechnology, chemical industry... On the contrary, with strong corrosion resistance, HELUTOP® HT-E steel cable glands are used in many heavy industries such as machinery construction, factories, robotics, shipbuilding, railway technology...
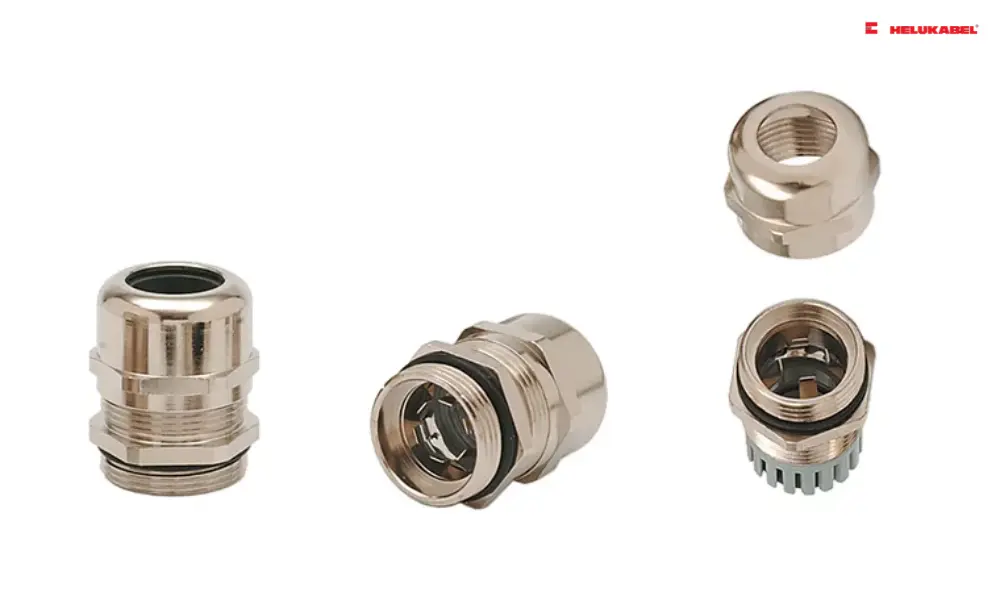



HELUTOP MS-EP cable gland
4.3 Brass cable glands
Brass cable glands are categorized by the following characteristics:
- The cap nut and gland body are made from nickel-plated brass.
- The terminal insert is made from polyamide PA6.
- The moulded seal is made from neoprene.
- The O-ring is made from Buna-N.
- The lock nuts are made from nickel-plated brass.
Some lines of HELUKABEL’s brass cable glands include:
- HELUTOP® HT-MS achieved VDE international certification, upgraded design with specialized materials, suitable for applications requiring high tightening, durability, and safety such as automatic technology chemistry, robot technology, railway technology, control cabinets...
- HELUTOP® MS-EP and HELUTOP® MS-EP4 are EMC nickel-plated brass cable glands. Particularly, the HELUTOP® MS-EP cable glands can be used for grounding, automatic secure connection when closed, excellent screening attenuation and current discharge.
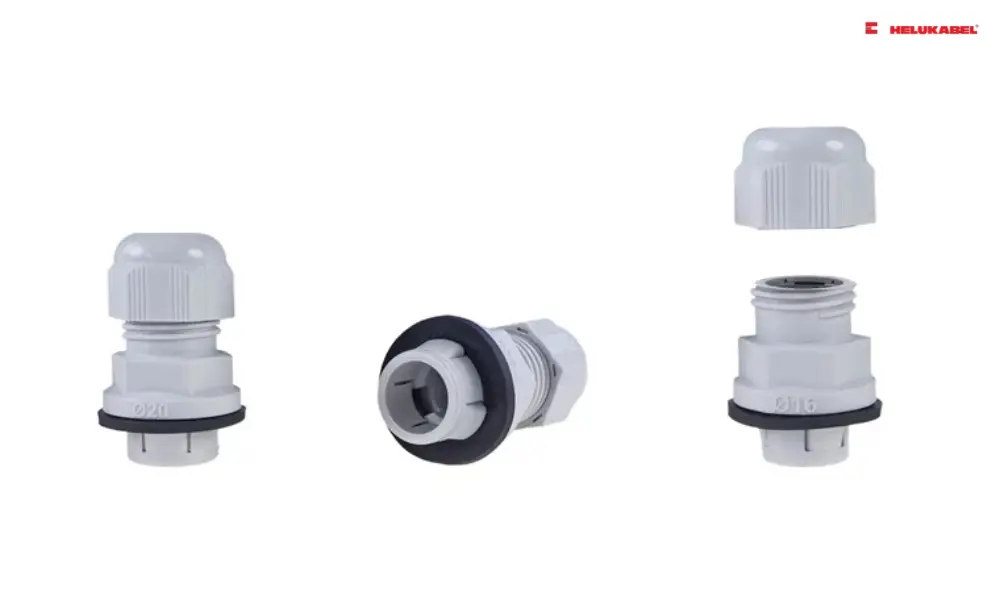

HELUTOP Easy threadless cable gland
4.4 HELUKABEL’s threadless cable glands
Threadless cable glands offer several advantages: installation is much easier, quicker and requires no tools. This makes threadless cable glands particularly attractive for panel building, allowing users to save time and money.
With the HELUTOP Easy product range, HELUKABEL offers threadless cable glands with clamping ranges from 5 to 21 millimeters. These have VDE approval in accordance with DIN EN 62444, the standard that defines all requirements for the construction and design of cable glands. Furthermore, they are UL-approved according to making them ideal for companies that export and want to minimize inventory by using components with multiple approvals. The housing is also certified to IP66/IP68, providing reliable protection against foreign objects and liquids.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
Tel. +84 28 77755578 | info@helukabel.com.vn | www.helukabel.com.vn






