Top 7 differences between flat cables and round cables
Flat cables and round cables are not only different in shape but also possess distinct characteristics in terms of structure, properties, and application range. Let’s explore these differences in the following article!
Contents:
1. Characteristics of round cables
2. Characteristics of flat cables
3. Comparing flat cables and round cables
4. Key applications of flat and round cables
5. HELUKABEL's product portfolio for flat and round cables
On the market, the most common type of cable is round cable. Meanwhile, flat cables have a distinct shape. But does their performance differ from that of round cables? Understanding the specific characteristics of each type will help you optimize durability, lifespan, flexibility, and space efficiency as needed. This article highlights the key differences between flat cables and round cables and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of each. With this knowledge, you will have a solid foundation to make the best decision for your application.
1. What are round cables? Characteristics of round cables
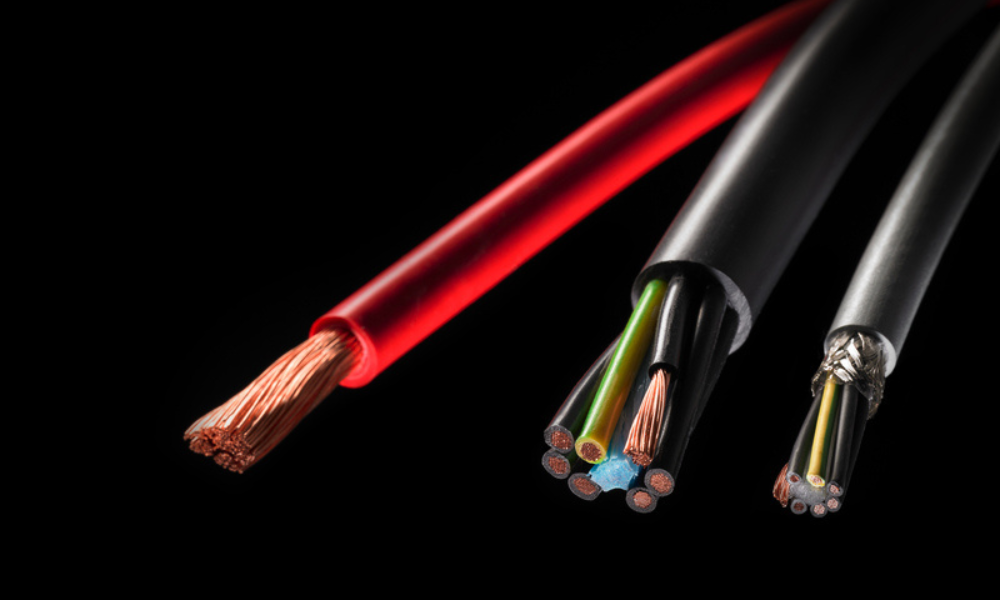

A round cable consists of electrical conductors arranged in a circular pattern. These conductors are insulated and filled with materials that maintain the cable’s cylindrical shape. Round cables can contain individual conductors or twisted strands. Regardless of the configuration, the conductors are arranged in a helical (spiral) structure around the cable’s axis with a specific twisting angle. The larger the twist angle, the greater the cable's flexibility.
The basic components of a round cable typically include:
- Conductor: The core component responsible for carrying electrical current.
- Insulation: Surrounds the conductor to prevent electrical leakage.
- Shielding: Reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) in certain applications.
- Outer sheath: The outermost layer that protects the cable, securing all internal components and providing resistance against environmental factors such as moisture, oil, and fire.
2. What are flat cables? Characteristics of flat cables

A flat cable consists of multiple individually insulated conductors that are precisely spaced and arranged in a straight line, all encapsulated within an insulating layer. This unique structure provides high flexibility, allowing the cable to bend easily even in tight spaces.
Unlike round cables, flat cables typically do not have filler materials or shielding layers. Shielding flat cables is challenging because the shielding layer struggles to maintain its flat shape and tends to curl up. As a result, standard electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding methods are less effective for flat cables.
Flat cables are commonly made from materials such as elastomer or silicone rubber, which provide softness, corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures, including cold environments. Additionally, their compact design helps reduce cable tangling and makes installation easier and more organized.
3. Top 7 differences between flat cables and round cables

3.1 Structure of flat cables and round cables
In terms of structure, flat cables have a flat shape, similar to a ribbon. Flexible flat cables typically consist of multiple fine copper strands, which may be twisted or braided together and arranged in parallel to form a flat surface. Thanks to this design, flat cables can bend more flexibly while maintaining the same number of conductors. Additionally, compared to round cables, flat cables offer better heat dissipation due to their larger surface area, which helps effectively reduce heat buildup.
In contrast, round cables have a cylindrical shape - the most common and traditional cable design. The conductors inside may be braided from multiple fine strands and twisted together to enhance flexibility and durability. This structure helps reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and minimizes signal loss during transmission.
Due to their structural characteristics, round cables generally provide better EMI protection compared to crane flat cables. Applying an overall shielding layer to flat cables is challenging because shielding materials tend to curl instead of maintaining a flat shape. This limitation makes flat cables more susceptible to external electromagnetic interference. Conversely, round cables inherently offer superior shielding against external EMI disturbances due to their natural design.

3.2 Flexibility
Flat cables can bend easily in specific directions, allowing them to adapt well to various shapes, sizes, and structures. This makes them particularly suitable for threading through corners or fitting into tight spaces - an ideal choice for confined environments.
While round cables may be less flexible in tight spaces, their cylindrical shape makes them easier to handle and install. Unlike flat cables, which can only bend in two main directions, round cables can bend in any direction. Thanks to this characteristic, round cables are preferred for applications requiring frequent bending and twisting over long cable runs, especially when installed in conduits or cable trays.
3.3 Signal quality and skewing
Due to their design and materials, round cables generally maintain better signal integrity. They are often equipped with effective shielding, which protects signals from external interference and ensures stable transmission in data, audio, or video applications.
Flat cables can still transmit signals effectively, but without proper shielding, they may be more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI). For high-precision electronic applications, round cables are often the better choice to ensure optimal performance.
Signal skewing occurs when electrical signals travel at different speeds within the same conductor pair. Flat cables tend to minimize skewing better than round cables. Due to high manufacturing precision and symmetrical conductor arrangement, flat cables ensure that all conductors have identical electrical and physical lengths within a continuous dielectric layer. These factors help reduce time delays between signals, leading to more stable and synchronized transmission.
3.4 Durability and enviorenmtal resistance
Cables are exposed to various environmental factors that can degrade their performance over time if not manufactured with the right materials. These factors include UV exposure, oils, radiation, abrasion, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stresses such as friction, twisting, repeated bending, reciprocating motion, and S-bends. Thanks to their ability to bend in multiple directions, round cables can withstand these stresses better, leading to longer lifespan and durability in harsh working environments.
Most PVC or PTFE materials used in round cables can be engineered for superior resistance to these environmental factors while maintaining flexibility. In contrast, silicone-extruded flat cables can endure high temperatures. However, silicone is soft and has lower abrasion resistance, making it more susceptible to wear, which could expose internal conductors and lead to potential failures.
Although flat cables excel in handling repetitive bending along a fixed axis (rolling flex), they offer greater uniformity and reliability in conductor alignment. Due to their simpler structure compared to round cables, flat cables have fewer connection errors during installation, reducing operational risks.

3.5 Space efficiency: a key advantage of flat cables
Flat cables provide a clear advantage in space optimization. Their flat design allows them to be packed more efficiently than round cables, maximizing installation space. Additionally, flat cables offer greater flexibility for bending and folding, making the most of available space.
In contrast, round cables often leave unused gaps around them due to their limited bending capabilities, making them less space-efficient in confined installations.
Thanks to their flexible design, flat cables are easier to route around pulleys and sheaves, making them particularly suitable for crane operations, where they must endure repetitive loading and unloading cycles.
3.6 Cost consideration
Flat cables are engineered for high flexibility and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements in various applications. However, to ensure smooth movement, flat cables require careful weight balancing during manufacturing. This process demands specialized tools to encapsulate all components into a single cable, leading to higher production costs compared to round cables, which follow standardized industry manufacturing processes.
Although round cables are generally cheaper upfront, they are prone to tangling, heat dissipation issues, and faster wear, potentially leading to higher long-term operational costs due to frequent replacements.
3.7 Maintenance and repairs
When it comes to repairs or component replacements, round cables are easier to handle, as technicians can work on them without requiring specialized tools. This results in minimal downtime for machinery and equipment.
Conversely, repairing or replacing flat cables requires special tools to reassemble the components into a single cohesive unit, making maintenance more time-consuming and potentially causing longer production downtime.
4. Applications of flat cables and round cables

4.1 Key applications of round cables
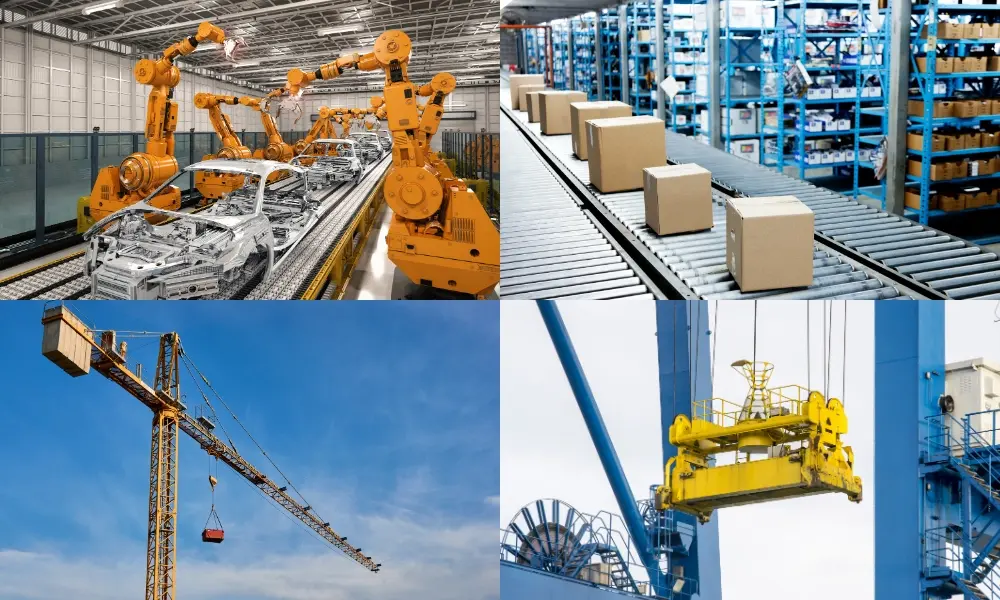
Round cables are particularly suited for applications requiring high durability, environmental resistance, and enhanced protection, including:
- Industrial automation: Widely used in robotics, CNC machines, and factory automation systems.
- Communication networks: Round Ethernet cables such as Cat5e and Cat6 enable high-speed data transmission in LANs, WANs, and data centers. Their symmetrical structure and shielding ensure stable signal transmission and minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Outdoor and harsh environments: Some round cables feature thick protective jackets and waterproofing, making them ideal for construction sites, offshore oil rigs, and wind farms.
- Material handling and waste processing

4.2 Key applications of flat cables
With a thin, flat design, flat cables are highly flexible and can bend easily in tight spaces without breaking or getting damaged. Common applications include:
- Telecommunications: Flat cables are ideal for telecommunication systems, where cables must be installed in confined spaces with complex arrangements. Their space-saving design simplifies cable management in limited installation areas.
- Robotics: Modern robots have compact and intricate structures, requiring lightweight and flexible wiring. Flat cables help optimize space and prevent cable twisting or interference with robotic movement.
- Overhead cranes: Some overhead crane systems use flat cables instead of round cables due to space constraints and the need for continuous bending. Flat cables efficiently deliver power and control signals while maintaining durability and flexibility in demanding work environments.
5. HELUKABEL’s flat cables and round cables
Understanding the differences in structure, characteristics, and application scope of each cable type helps you choose the optimal cable solution, ensuring performance, safety, and cost efficiency for your electrical system.
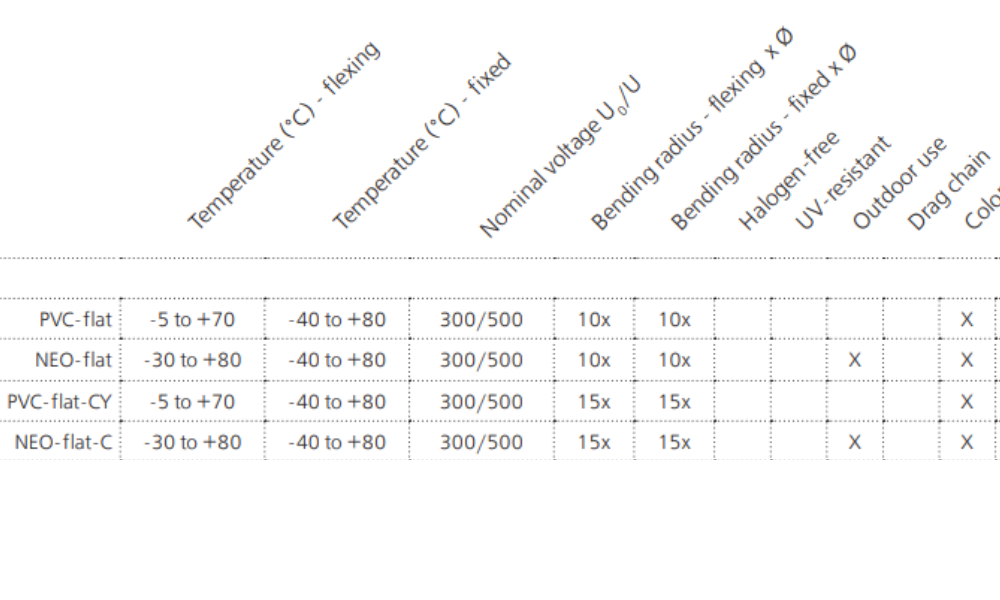
HELUKABEL's extensive product portfolio includes a wide range of round and flat cables, catering to various industrial applications. Some of HELUKABEL’s notable crane flat cable series include:
- PVC Flat Cable – Flat
- PVC Flat Cable – Flat CY
- NEO-flach Flat Cable
- NEO-flach Flat Cable CY
For round cables, with a catalog of over 10,000 product codes, you can discover our product portfolio for cables and wires .
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |







