What are CVV cables? A comparison between CVV cables and CXV cables
CVV cables and CXV cables are prevalent, yet they can often lead to confusion. The following article aims to draw a line between these two.
1. What are CVV cables?
1.1 Overview of CVV cables
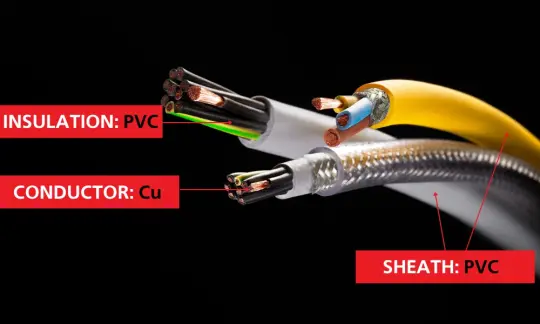
CVV cables are specialized cables utilized for transmitting voltage in civil and low-voltage electrical systems. The "CVV" designation of the cable indicates that it is composed of copper, insulation and outer sheath are constructed from PVC material. Within this designation:
- "C" signifies copper, the material constituting the electrical conductors.
- "V" denotes PVC, the material utilized for insulation and the outer sheath of electric cables.
Depending on the intended application, users can select from a range of configurations including 2-core, 3-core, 4-core, 3+1, or 4+1 cables.
1.2 Characteristics of CVV cables
With that structure, CVV cables exhibit the following technical characteristics:
- CVV cables can withstand a voltage level of U0/U: 0.6/1kV.
- Test voltage: 3.5 kV (for a duration of 5 minutes).
- Operating temperature range: 140°C (for cross-sections exceeding 300mm²), and 160°C (for cross-sections equal to or less than 300mm²).
1.3 Applications of CVV cables
CVV cables find application in the control systems of numerous facilities, encompassing power stations and transformer stations. Moreover, they serve in monitoring systems for electrical equipment, control apparatus, automation systems, electrical machinery, and control circuits within power plants. Additionally, cvv cables are suitable for outdoor installations or in dry or damp cable trenches. They can be mounted on cable ladders, trays, or within ducts along insulated walls. Furthermore, they are suitable for underground ducts, spanning from the power source to machinery or equipment, as well as for use within workshops and buildings.
>>Find out more: Identify the quality of control cables
2. What are CXV cables?
2.1 Overview of CXV cables
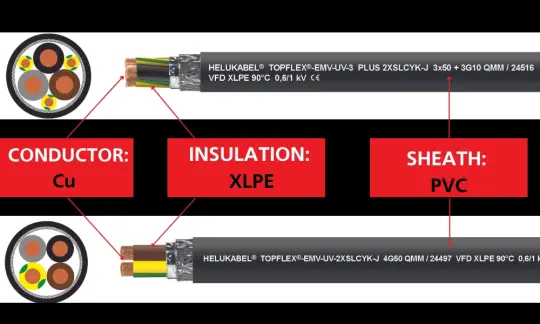
CXV cables are employed in low voltage electrical systems, capable of transmitting voltage levels of 0.6/1kV. The "CXV" designation of the cable indicates that it comprises copper conductors, an insulation layer utilizing XLPE material, and a PVC sheath. Within this designation:
- "C" denotes copper, utilizing high-purity pure copper to enhance the electrical conductivity of the cables.
- "X" represents XLPE, an insulating material fabricated from polyethylene plastic, suitable for high-temperature applications.
- "V" signifies PVC, which serves as the outer sheath of the electric cables.
2.2 Characteristics of CXV cables
With that structure, CXV cables exhibit the following technical characteristics:
- Excellent conductivity
- Capable of supplying power at voltage levels of 0.6/1kV CXV cables are equipped with XLPE insulation, providing them with high heat resistance.
- The conductive core can operate normally at temperatures of up to 90 °C.
- Effective in preventing the spread of fire.
2.3 Applications of CXV cables
CXV cables are extensively utilized in daily life, particularly in construction projects, with specific applications including:
- CXV cables find frequent use in industrial equipment such as industrial electric fans and industrial air conditioners.
- CXV cables are also used in the realm of mechanical engineering, manufacturing, factories…
- In civil projects, CXV cables are utilized in various settings such as shopping centers, residences, offices, and schools.
3. A comparison between CVV cables and CXV cables

Though sharing a certain degree of resemblance, CVV cables and CXV cables exhibit distinctive differences:
- Flexibility: CVV cables demonstrate greater flexibility compared to CXV cables. This stems from the fact that CVV cables possess superior bending capabilities, rendering them easier to install in confined spaces. Conversely, CXV cables tend to be stiffer, necessitating meticulous calculation prior to installation.
- Mechanical strength: In this regard, CXV cables boast superior mechanical durability owing to their impact resistance. Additionally, the inclusion of XLPE sheathing enhances CXV cables' capacity to withstand high temperatures and provides commendable fire resistance.
- Power transmission performance: When comparing cables with identical cross-sectional areas, CXV cables exhibit superior power transmission capabilities to CVV cables. This superiority arises from the XLPE insulation material utilized in CXV cables, which offers enhanced electrical carrying capacity compared to PVC material found in CVV cables.
- Lifespan of electric cables: The longevity of electric cables hinges on various factors including product quality, construction and installation processes, environmental conditions, and the frequency of cable inspection and maintenance. However, CXV cables typically boast a longer lifespan due to their utilization of higher quality materials.
- Product price: CXV cables often command a higher price than CVV cables due to their numerous superior attributes. These include the ability to withstand higher temperatures, superior electrical load capacity, extended lifespan, and the production of less non-toxic smoke when burned.
4. Frequently asked questions about CVV cables and CXV cables
4.1 Which one is better, CVV cables or CXV cables?
Assessing the suitability between CVV cables and CXV cables depends on the specific application at hand. Consequently, in determining whether CVV cables or CXV cables are more appropriate, users must consider various factors. Some typical considerations include the number of cores, cross-section, environmental conditions, technical requirements, and standards applicable to the project.
4.2 Which one of these two is best suited for outdoor environments?
Proven to be better at mechanical durability, CVV cables are a more suitable choice for outdoor applications. Equipped with a sheath made from XLPE, CXV cables can withstand environmental factors such as temperature variations, rainwater, and humidity.
>>Find out more: Different types of frequently used cable
5. Product comparison: NYY cable and N2XH cable
In this article, HELUKABEL will introduce two cable lines NYY and N2XH as well as the similarities and differences between these two:


| Criteria | NYY (CVV cable) | N2XH (CXV cable) |
| Standard compliance | Ensure compliance with the quality standards, including DIN VDE 0276-603/HD 603 S1/IEC 60502 (for the NYY cable line) and DIN VDE 0276 part 604, HD 604 S1 part 1 and part 5G (for the N2XH cable line). The bare copper conductor is in accordance with DIN VDE 0295 class 1 or class 2/IEC 60228 class 1 or class 2 standards. | |
| Temperature range | Functions effectively within the temperature range of -5°C to +50°C while flexing. Under fixed installation conditions, N2XH cables perform optimally within the temperature range of -30°C to +90°C, whereas for NYY cables, this parameter ranges from -40°C to +70°C. | |
| Minimum bending radius | In both NYY cables and N2XH cables, the minimum bending radius is 15 times (for single-core wire) and 12 times (for multi-core wire) the outer diameter of the core. | |
| Nominal voltage |
| |
| Radiation resistance | Inapplicable | The N2XH cable line has radiation resistance properties of up to 100x106 cJ/kg (up to 100 Mrad), helping the cable maintain its performance when operating in high radiation-rich environments. |
| Permissible conductor operating temperature | +70°C | +90°C |
| Applications | Are installed in open air, in underground, in water, indoors, in cable ducts, power stations, for industry and distribution boards as well as in subscriber networks, where mechanical damages are not to be expected. | In environments with many potential risks of fire and explosion in power plants, industrial buildings, public facilities, airports, train stations, hospitals, multistorey buildings, process control centers... Suitable for permanent installation in dry and wet environments, in, above, and beneath plasters as well as in masonry walls and in concrete. |
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
Tel. +84 28 77755578 | info@helukabel.com.vn | www.helukabel.com.vn