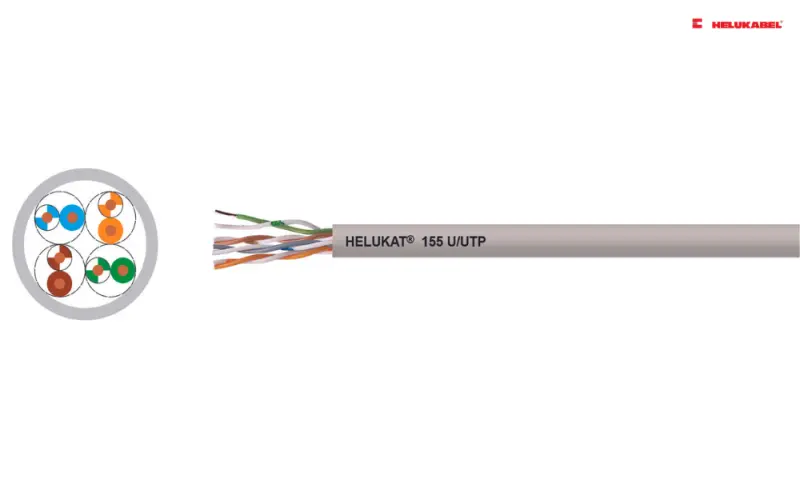
What are data cables? How to select the correct data cables
Data cables with many different types can easily confuse users. Let's learn basic information about data cables and HELUKABEL’s data cables through the following article!
Not all data cables are the same. Many users do not realize this until they are experiencing disruptions and errors in the data transmission in their industrial applications. In this article, you will learn what the most common mistakes are when selecting an industrial Ethernet or bus cable and how to avoid them.
>>See more: Data, network, and bus technology
1. What are data cables?

Data cables are physical media used to transmit data and provide power between electronic devices. It acts as a bridge, allowing communication and power transfer between devices that may have incompatible ports or functions. Data cables are designed with specific connectors at each end, ensuring safe and efficient data transmission.
In the industrial sector, data cables play a vital role in ensuring fast and effective data communication and automation. This infrastructure is used to manage a business's technology needs, from computer networking and wireless Internet to video/audio cabling, fiber optic cable installation, and data center installation.
>>Find out more: Industrial ethernet and data cables
2. A glance at data cables

2.1 Characteristics of data cables
All cables and wires that contribute to communication in any way are commonly referred to as data cables. There are, however, significant differences, such as the completely different structures of copper and fibre optic cables. Copper data cables come in many different types, such as low-frequency cables, coaxial, telephone, and bus cables, diverse Ethernet systems, or microwave cables for special applications requiring transmission in the range of gigahertz. Selecting the wrong cable can quickly lead to costly disruptions and errors.
2.2 A comparison of cable insulation materials
| Material | VDE-Label | Dielectric Constant | Halogen free |
| PVC | Y | 3.6-6 | no |
| PVC +90°C | Yw | 4-6.5 | no |
| PE | 2Y | 2.3 | yes |
| PE foamed | 02Y | 1.6-1.8 | yes |
| PP | 9Y | 2.3-2.4 | yes |
| PP foamed | 1.6-1.8 | yes | |
| PUR | 11Y | 4-7 | yes* |
| FEP | 6Y | 2.1 | no |
| *Dependent on flame retardants used | |||
In general, data cables are low-capacity cables. This means that as little electrical energy is accumulated in the cable as possible when transferring data. This electrical energy has a negative impact on the signal quality. The capacity is in part dependent on the insulation material of the cable. Modern bus and Ethernet cables primarily use materials such as PE or PP, which provide especially good insulation, which is determined by measuring the dielectric constant (εr). The lower this value is, the better the material is at insulating, and the lower the capacity of the cable. This is why thinner insulation can be used when the same dielectric strength is used.
Pristine data transmission is achieved through the correct cable construction. A solid wire, which is perfectly round and has a uniform diameter, offers the best electrical performance. For industrial Ethernet and bus cables, construction according to the AWG is preferred since this flexible construction results in a round conductor. Metric cables are not suitable for this application since they have a bunched construction and are not round. This results in variable capacities which heavily impair high-frequency data transmission.
>>Find out more: What are AWG and AWG cables?
3. Common Errors when Selecting Industrial Ethernet and Bus Cables

Poor decoupling (left) and good decoupling (right)
3.1 Low-Frequency Cables for High-Frequency Applications
Selecting low-frequency cables for high-frequency Ethernet connections is a common cause for malfunctions in the transmission of data. These cables are also low capacity but exhibit a different characteristic impedance as what is required by the Ethernet standard. This results in a mismatch, or a discontinuity. In low-frequency data cables, all pairs are laid in parallel strands. This means that all four lay lengths are the same. Ethernet cables used in high-frequency applications must also be optimally decoupled. This is achieved by using four different lay lengths, which are individually measured. The positions of the twisted pairs within the overall construction must also be taken into account.
3.2 Classic Stranded Pairing instead of a Star Quad
Many industrial communications standards, such as PROFInet, EtherCAT, or SERCOS III, use cables with two twisted pairs, which are twisted into what is called a star quad, for data transmission. Here, all four cores are stranded in a perfectly round shape. The benefit of this is that it leads to no differences in transit time. This differs from the classic stranded pairing, where the individual twisted pairs must have two different stranded lay lengths due to the required decoupling. If the incorrect twisted-pair cable is used, it could lead to problems with transmission and transit times.
In star quads, the cores that are diagonally opposite from each other form the electrical pair. If this rule is ignored when connecting the cable, the characteristic impedance and the near-end crosstalk (NEXT) of the cable are changed, which may reduce the transmission quality, as well. Even screened, four-core sensor cables are not suited for use as high-frequency industrial Ethernet or bus cables, despite their construction appearing comparable at first glance. The difference being that the core insulation strength is not intended for Ethernet, and the stranding is not perfectly round in construction. This results in an inadequately functioning cable due to unsuitable characteristic impedance, NEXT, and cable attenuation.

2 Pairs
- 4 x Core diameter
- 3 x Stranding
- Pairs according to illustration
- Straightforward
- Different signal transit times

Star Quad
- 2.4 Core diameter
- 1 x Stranding
- Diagonal cores create the electrical pair: white/blue and orange/yellow
- Identical signal transit times

3.3 Too Long of Cable or too Small of Diameter
Another classic example are segments that are too long. According to the Ethernet standard, a repeater must be used after maximum 100 metres of length. This receives the weak signal and transmits it again at full strength. In practice, segments with lengths longer than 100 metres can be found, however these are not in accordance with the applicable standards. In these cases, rising temperatures, aging, and other factors could quickly lead to defects or failures. Thinner cables with AWG 26 diameters are limited to 60 - 70 metres. It is important to remember that every plug connector is a joint that causes loss via attenuation and reflection, which reduce the range.
>>See more: Why conductor's cross sections are important?
3.4 Incorrect Plug
It is a common occurrence that non-standard and untested plugs are used in Ethernet applications, such as D-Sub or M12 plugs, which are A-coded with an 8-pin design. These plugs do transmit data, however the quality is significantly reduced due to the lower near-end crosstalk (NEXT). The reason for this is the positioning of the middle pin, which is not in accordance with standards and impedes data transmission.
According to Ethernet standards, admissible connector faces for the best data cabling are screened plugs/sockets:
- RJ45 4-pin (100 Mbit 4-pin)
- RJ45 8-pin (Gbit 8-pin)
- D-coded M8 & M12 (100 Mbit)
- A-coded M8 4-pin (100 Mbit)
- P-coded M12 (100 Mbit)
- X-coded M12 (Gbit)
- Ix Industrial (Gbit)
- Mini-IO
- SPE (Single Pair Ethernet)
Furthermore, there are varying standards such as PROFInet, EtherCAT, or SPE (Single Pair Ethernet) that can transmit data and power in one hybrid plug. These either adhere to IEC norms, have been evaluated by the appropriate organisations, or are being standardised.
Standardised Hybrid Ethernet Plugs
- M8 SPE acc. to IEC 63171-6
- M12 SPE acc. to IEC 63171-7
- Y-coded M12 acc. to IEC 61076-2-113
- M23 acc. to IEC 61076-2-117
- RJ45 Hybrid acc. to IEC 61076-3-106
- Ix Industrial acc. to IEC 61076-3-124
Certain plug manufacturers have their own hybrid solutions in their portfolios that are not standardised but have been tested and evaluated for Ethernet conformity. As a basic principle, it is suggested to always stick to standardised and evaluated Ethernet plug connectors.
4. HELUKABEL’s data cables

4.1 Optical fibre cables
Optical fibre cables are made of glass or plastic that uses light to transmit signals and networks. This type of data cable exhibits the following outstanding characteristics: high transmission rates, low attenuation, no electromagnetic problems, small dimensions and low weight. The HELUCOM® optical fibre cables are manufactured in accordance with the standards and regulations of DIN VDE 0888.
A-DF(ZN)2Y(SR)2Y optical fibre cables are characterized by a stranded construction with jelly filling. Above-average rodent protection is achieved with the metallic rodent protection (corrugated steel) and the second outer sheath made of PE. This construction is particularly used in the area of telecommunication and long distance, but also in regular channels and tubes where rodent infestation is possible.
HELUCOM® A-DQ(ZN)B2Y, central are characterized by a design that is particularly easy to mount and is rodent-protected. In addition, these cables are designed grease-free. This construction is particularly used in underground, tubes and channel areas, where normal tensile stresses and/or transverse compressions occur, and rodent infestation is to be expected.
4.2 HELUKAT data cables
All HELUKAT® data cables and wires comply with the latest standardization recommendations and are designed for use in high-speed networks with transmission rates of 100 Mbit/s and higher. HELUKAT® data cables meet the requirements of category 5 according to EIA/TIA TSB-36 ISO/IEC DIS 11801, CENELEC pr EN 50173, as well as category 6/7 according to DIN 44312-5/ EN 50288.
Some lines of HELUKAT® data cables include:
- HELUKAT® 155 CAT.5e U/UTP PVC STATIC: are characterized by large performance reserves and outstanding performance. They can be used to implement services such as Fast Ethernet, Ethernet, ATM155, FDDI, token ring 4/16 Mbit/s, or ISDN absolutely trouble-free.
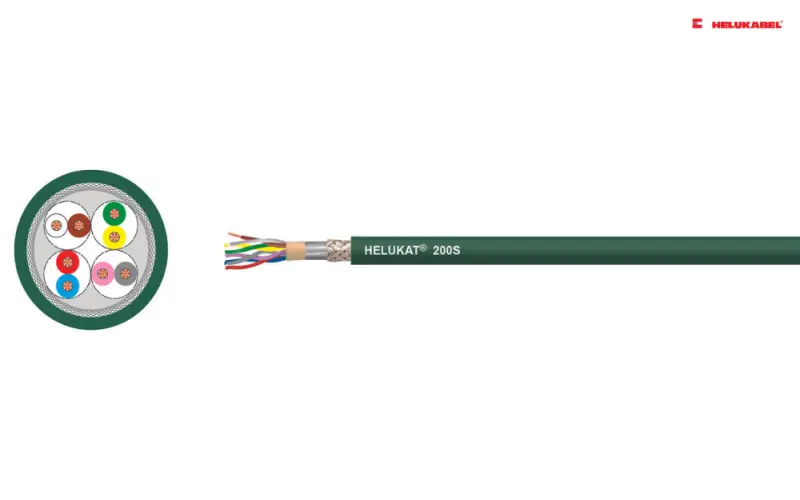
- HELUKAT® 200S CAT.5 4P SF/UTP PUR CHAIN green: is designed for use in cable carriers and the extreme loads caused by moving machine components and provides excellent transmission characteristics under the most difficult and extreme conditions. Thanks to the clever structure, it is also suitable mechanically for use even in cable carriers with a high packing density.
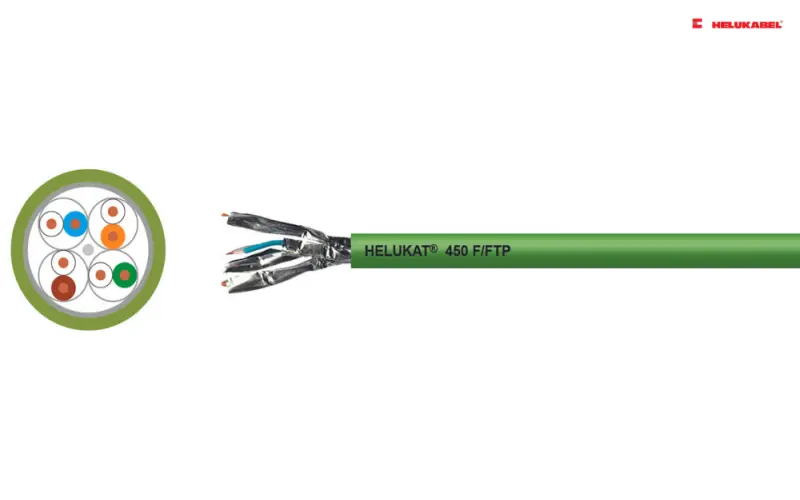
- HELUKAT® 450 can be used to implement services such as Gigabit Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Ethernet, ATM155, FDDI, token ring 4/16 Mbit/s or ISDN absolutely trouble-free.
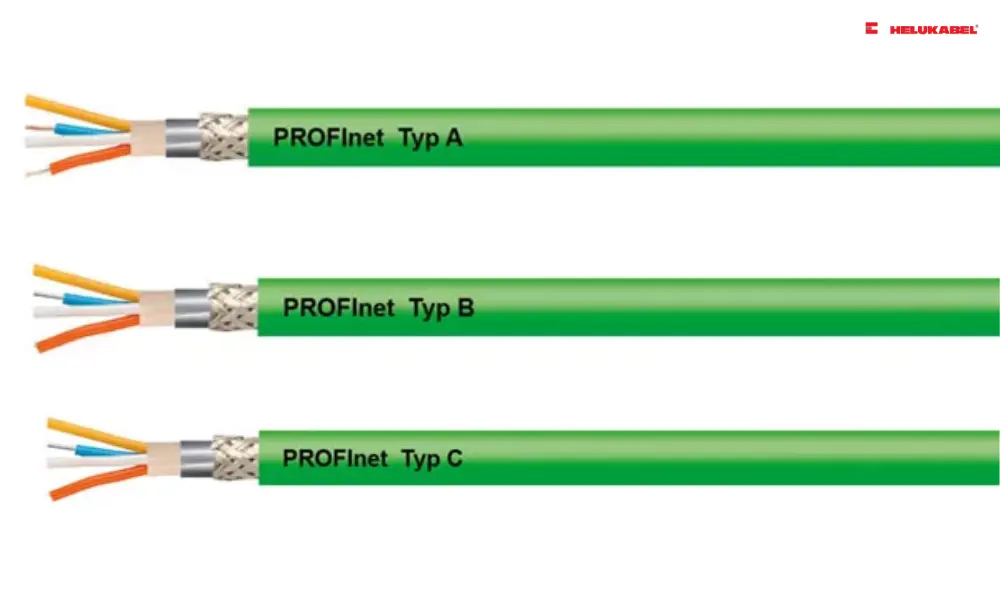

4.3 Bus cables
Bus technology is being used in an increasing number of industrial applications. The information from the master controller is sent over a bus network and is potentially available to all components in the system.
HELUKAT® PROFInet A CAT.5e SF/UTP PVC STATIC are highly flame-retardant, resistant to oil, UV radiation, weathering effects, microbes. In addition, it guarantees excellent transmission characteristics and may be used even under the harshest conditions.
HELUKAT® PROFInet B CAT.5e SF/UTP FRNC FLEX are highly flexible and can be used in areas that demand halogen-free characteristics.
HELUKAT® PROFInet C CAT.5e SF/UTP PVC CHAIN receives UL CMG PLTC FT4 AWM 600V approval, exhibits the following characteristics: highly flame-retardant, notch-resistant and abrasion resistant. This cable can withstand mechanical loads, suitable for moving parts and drag chains.
>>See more: A glance at structure and applications of PROFInet cables
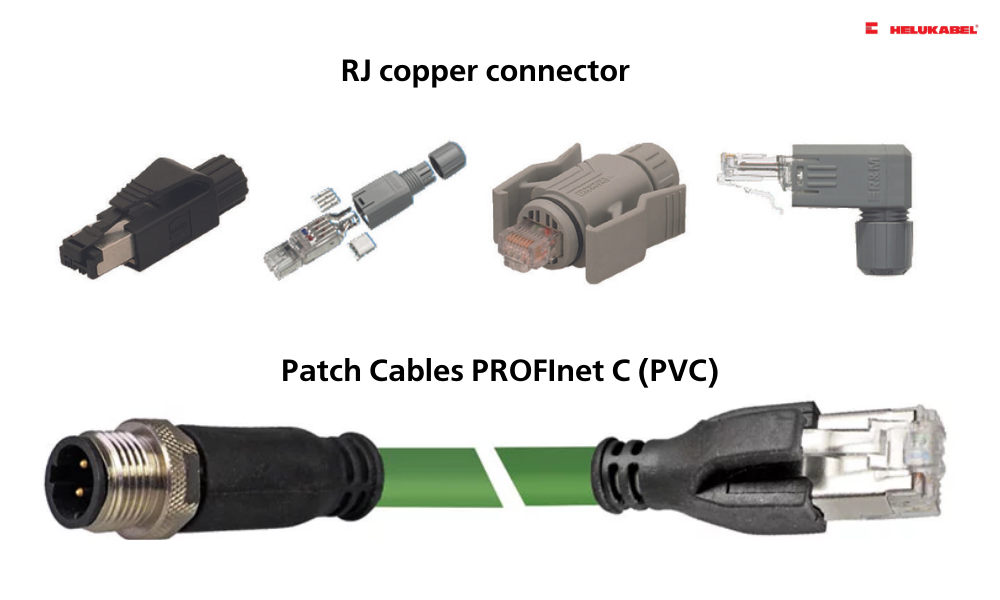
4.4 Connecting solutions for data cables
In addition to active components and cables, connecting solutions for data cables are also provided. The complete connecting system helps to ensure the full reliability and state-of-the-art functionality of the structure building wire. HELUKAT CONNECTING SYSTEMS from HELUKABEL provides passive copper connection components such as patch panels, patch cable, RJ 45 socket, RJ 45 cooper connector, M12 copper connector…
Besides, pre-assembled cables from HELUCOM CONNECTING SYSTEMS provide customers with economical, yet high-quality solutions.
When selecting data cables for industrial applications, users should adhere to the appropriate standards in order to prevent failures and malfunctions. Users must also pay attention to the lengths of the individual segments, the number of plugs, and the different diameters of installation and patch cables. Furthermore, the aging of individual components can, in the long term, lead to a reduction in the transmission quality and to interruptions. With 45 years of experience, HELUKABEL is an expert in connection technology and is happy to support users in identifying the perfect industrial Ethernet or bus cables for their industrial application.
5. HELUKABEL's data cable price list (Updated)
HELUKABEL offers a wide range of data cable products to meet the diverse needs of customers. Each type of audio cable comes with a different price, depending on factors such as the number of cores, cross-sectional area, and jacket material. For advice on choosing the right data cable and receiving the most accurate price quote, please contact HELUKABEL Vietnam's team of engineers directly.
Below is the reference price list for some HELUKABEL's data cables:
| Type of data cables | Unit | Reference price (VNĐ/m) |
| PAAR-TRONIC-CY data cables | Meter | |
| TRONIC (LiYY) data cables | Meter | 19.800 - 41.000 |
| PAAR-TRONIC-CY (LiY-CY) data cables | Meter | 38.700 - 43.000 |
| HELUKABEL PAAR-TRONIC-Li-2YCYv data cables | Meter | 93.600 - 104.000 |
| HELUDATA UL 20276 | 2 X 2 X 22 AWG data cables | Meter | Around 35.100 |
| HELUDATA UL 2464 | 1 X 2 X 18 AWG data cables | Meter | Around 42.300 |
| HELUDATA UL 2464 | 1 X 2 X 16 AWG data cables | Meter | Around 53.100 |
| HELUDATA UL 2919 | 1 x 2 x 24 AWG data cables | Meter | Around 37.800 |
Note: The electrical cable prices provided above are for reference only and may vary depending on the specific time. For the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information, please contact HELUKABEL Vietnam’s sales team.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
Tel. +84 28 77755578 | info@helukabel.com.vn | www.helukabel.com.vn