Understanding AWG cables and their importances
AWG cables are a familiar concept for users following the AWG system. So, what are AWG cables, and what should be known about it? Let's explore in the following article!
When it comes to cable diameter, users need to be familiar with both the AWG system and the metric measurement system. The AWG system is prevalent in the U.S to indicate the diameter of electric conductors, while the metric system is used in many other parts of the world.
1. A glance at AWG cables and metric system
1.1 What are AWG cables?
AWG (American Wire Gauge) is the U.S. standard for measuring the diameter of electrical conductors. This system differs from the metric system, which is based on the cross-sectional area of the wire (measured in mm²) according to the IEC 60228 standard. The larger the AWG number, the smaller (or thinner) the wire diameter. For example, AWG 10 cable has a larger diameter than AWG 20 cable. This system makes it easy to determine wire sizes based on their numeric value. The size range in the AWG system spans from 0000 (4/0), the largest, to 40, the smallest.
For AWG cables larger than 1, the diameter is indicated using the term "aught." As the number of "aughts" increases, so does the wire's thickness. There are four "zero" or "aught" sizes as follows:
- AWG 1/0
- AWG 2/0
- AWG 3/0
- AWG 4/0
These larger diameter single core cables are typically used in industrial environments and large residential applications, such as input power cables for electrical systems.
1.2 The metric system
In contrast, the metric system uses millimeters to measure the diameter of cables. This system is more precise than the AWG system and is commonly used in industries that require high accuracy. For example, a cable with a 2.5mm diameter is larger than one with a 1.5mm diameter.
When selecting electrical wires or cables for a specific application, it is important to consider the AWG size or the metric size to ensure compatibility with the equipment. Understanding the differences between these two systems can help prevent mistakes and ensure the proper functioning of the electrical system.
2. The importances of AWG in selecting cables
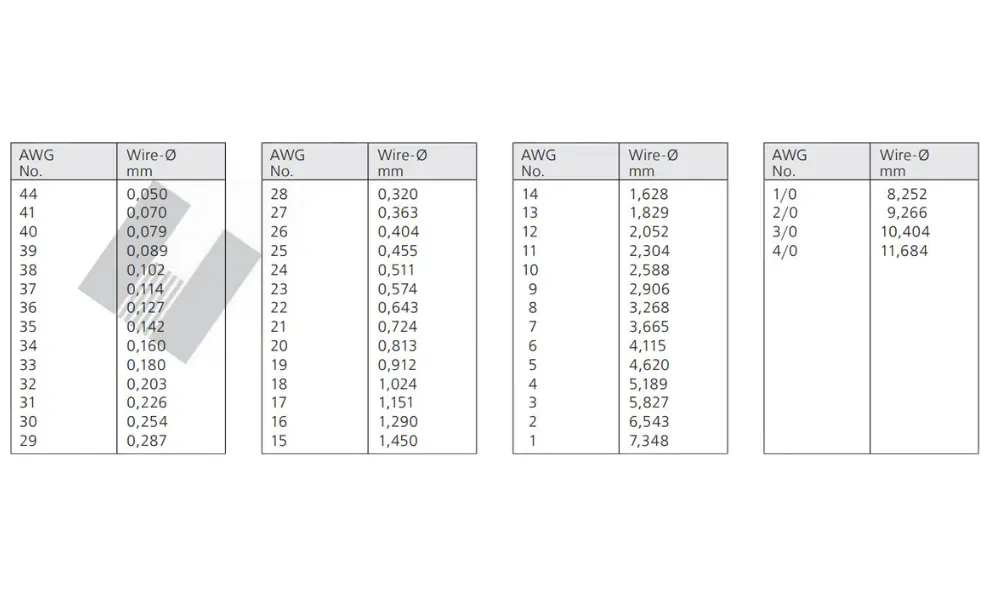
Coverting awg to mm2
The AWG rating plays a crucial role in selecting the right electrical cable for specific applications, ensuring the safety and performance of the electrical system.
2.1 AWG and its relation to electrical conductivity and power transmission efficiency
Wire diameter, as indicated by the AWG number, directly affects a wire's ability to conduct electricity and transmit power efficiently. Larger wire diameters (with smaller AWG numbers) allow more electricity to flow, reducing power loss when transmitting over long distances. This is particularly critical in high-power systems, such as industrial settings or large factories, where wires must handle high currents while maintaining optimal performance.
2.2 Ensuring electrical system safety
AWG ratings also provide important information about a wire’s current-carrying capacity. Wires with smaller AWG numbers (thicker conductors) have a larger cross-sectional area, allowing them to carry higher currents without overheating. Conversely, thinner conductors with larger AWG numbers have a smaller cross-sectional area and therefore a lower current-carrying capacity. Selecting cables with the correct AWG size is essential to prevent overloading. Wires that are too small in diameter (with large AWG numbers) will not be able to carry the required current, which can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards. Electrical safety regulations specify minimum wire sizes for each application to ensure cables are used safely and efficiently.
2.3 Reducing voltage drop
The AWG rating also relates to the conductor's resistance. Resistance affects both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), leading to a "skin effect," which reduces the effective cross-sectional area of the conductor and increases resistance. Wires with larger diameters (smaller AWG numbers) have lower resistance, which helps to minimize voltage drop. This ensures that electrical devices receive the correct voltage needed for stable operation.
3. Common types of AWG cables

Cables with bigger AWG (thin conductors) are typically suited for low-power, low-voltage applications, while cables with smaller AWG (thicker conductors) are necessary for systems with higher current and power demands. Therefore, users should refer to relevant electrical codes and standards and seek expert advice when needed to ensure the correct conductor size is chosen for any installation or electrical project. Some common AWG cable types include:
- 18 AWG: This is a thin wire, with a diameter of approximately 1.02 mm, often used for low-voltage applications such as doorbells, security systems, and thermostats.
- 14 AWG: A standard size for many residential applications, including 15-amp lighting circuits, bedroom outlets, offices, and general household wiring.
- 10 AWG: A thicker wire suitable for 30-amp circuits, electric dryers, small ovens, and window-mounted air conditioners.
- 8 and 6 AWG: These are the largest wires typically found in homes, used for high-current applications such as central air conditioning systems, electric stoves, and electric vehicle charging stations. In industrial settings, 6 AWG cables are used for applications requiring higher current capacity, such as heavy machinery, industrial furnaces, and large motor circuits.
- 4 AWG and larger: These are very thick wires commonly used for large industrial equipment, main power cables, EV chargers, and subpanels.
4. A few notes for users prior to the selection of AWG cables
4.1 AWG conversion table
The AWG conversion table is used to convert the size of electrical conductors based on the AWG standard into other parameters, such as wire diameter and cross-sectional area. This table helps users better understand the physical size of conductors based on the AWG rating. You can explore HELUKABEL’s AWG conversion table here.
Some information provided by the AWG conversion table includes:
- Wire diameter (AWG): This is the AWG rating of the conductor, indicating its size. Smaller AWG numbers (e.g., 0000 or 4/0) represent larger wire diameters.
- Wire diameter (mm): The external diameter of the conductor, measured in millimeters.
- Cross-sectional area (mm²): The cross-sectional area of the conductor, which reflects its ability to carry electrical current. A larger cross-sectional area allows for higher current capacity.
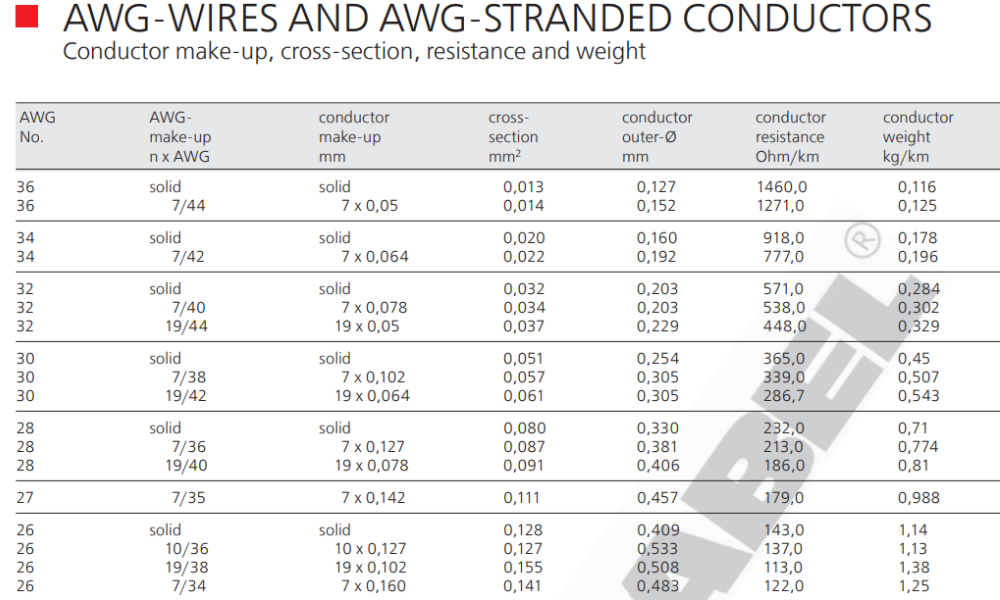
4.2 Are AWG ratings the same for solid and stranded cables?
When using the AWG conversion table, it's important to note that the information provided applies to solid conductors. For stranded wires, which are made up of many smaller strands, the AWG rating may indicate the size of each strand, but the overall cross-sectional area can be larger than that of a solid conductor with the same AWG rating.
AWG Make-up (n x AWG): This column shows the structure of the conductor. "Solid" refers to a solid core wire, while the format like "7/44" refers to stranded conductors, where the number before the slash indicates the number of strands, and the number after the slash shows the AWG size of each strand. For example, "7/44" means 7 strands of 44 AWG wire.
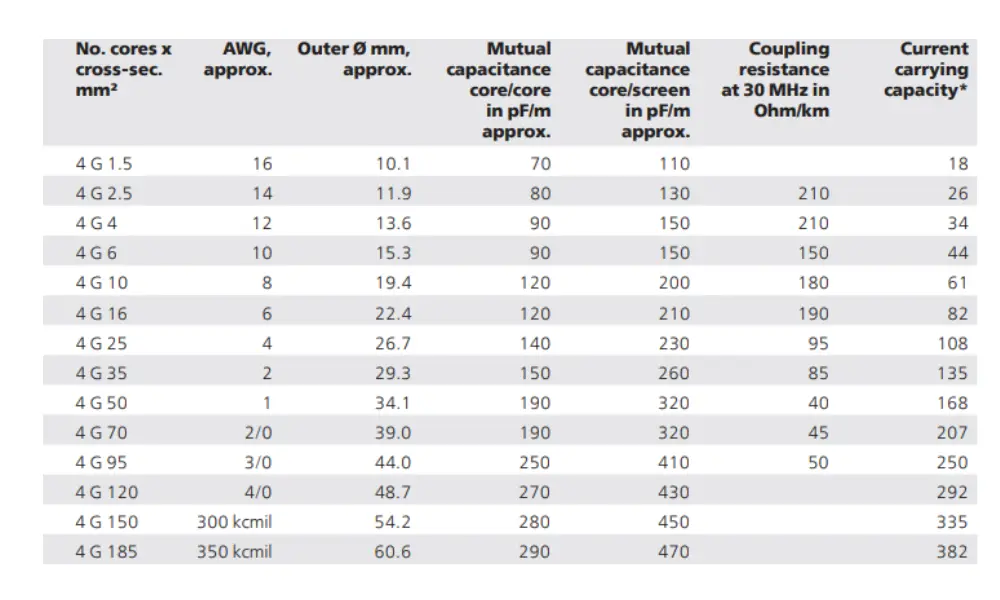
4.3 Using datasheets to choose the appropriate AWG cables
HELUKABEL datasheets provide detailed and accurate information about their electrical cable products, including AWG ratings and cross-sectional area (mm²). This information is essential for selecting the correct AWG cables for different electrical applications, ensuring system performance and safety. In addition, users can find other critical details such as voltage rating, operating temperature range, cable characteristics, and application scope
Common AWG cable products like 18 AWG control cables, 18 AWG audio cables, and 16 AWG signal cables are available on our online store. Users can place an order here !
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |