Advantages and disadvantages of wind energy
Wind power is a renewable energy source harnessed from the wind through wind turbines. Let's explore what wind energy is and its advantages and disadvantages in the following article.
Contents:
1. What is wind energy and wind farm?
2. Advantages and disadvantges of wind energy
3. Wind turbines: components and operating principles
4. Potential of wind energy in Vietnam
5. HELUKABEL’s cables for wind power projects
1. What is wind energy?

1.1 How is wind energy generated?
Wind is the movement of air caused by differences in atmospheric pressure on Earth, which mainly results from the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the Sun. When warm air expands, it creates a pressure imbalance with the cooler air nearby. The cooler air quickly moves in to fill this space - this movement is what we call wind.
Wind power, or wind energy, is a type of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity. The principle behind wind energy involves using wind turbines to convert the kinetic energy of moving air (wind) into electrical energy. Wind turns the blades of the turbine, which are connected to a generator inside a component called the nacelle (the housing unit at the top of the tower). As the blades spin, the mechanical energy is transferred to the generator, which converts it into electricity.
The electricity generated can be used directly for specific needs, such as powering streetlights or remote farms. Alternatively, it can be fed into the national power grid, where it is transmitted via power lines and cables to supply homes, businesses, and schools with electricity.
1.2 What is a wind energy farm?
Wind farms are groups of wind turbines - typically built on agricultural land or in rural areas. There are three main types of wind farms:
- Onshore wind farms: These usually consist of smaller-capacity wind turbines, making them convenient for grid connection and requiring lower investment costs.
- Offshore wind farms: Built in deep-water areas, these benefit from stronger and more stable wind speeds, ensuring higher electricity production efficiency.
- Distributed wind farms: This model involves installing wind turbines individually or in small clusters rather than concentrating them in large-scale wind farms.
2. Advantages and disadvantages of wind energy

Similar to solar power, wind energy has both advantages and limitations.
2.1 Advantages of wind energy
- Wind is a renewable energy source: Wind turbines harness energy from the wind by using rotational mechanisms to generate electricity. Wind is not only abundant and inexhaustible but also produces electricity without burning fuel or causing air pollution.
- Cost-effective electricity generation: Large-scale land-based wind turbines are currently one of the lowest-cost energy sources. Additionally, wind power continues to become more competitive due to advances in science and technology.
- Wind turbines can operate in diverse environments: Wind energy generation is well-suited for agricultural and multi-use land areas. It can also be deployed in remote and rural areas, farms, ranches, coastal regions, and islands where wind resources are plentiful.

2.2 Disadvantages of wind energy
- Ideal wind sites are often in remote locations: Delivering electricity from wind farms to urban areas with high demand poses installation and transmission challenges. Additionally, wind energy's stability and capacity depend on weather conditions.
- Wind turbines generate noise: While wind farms impact the environment differently than conventional power plants, concerns exist about the noise produced by turbine blades and their effect on the landscape.
- Transportation challenges: Wind turbines are becoming larger to improve energy efficiency. However, this makes transportation and installation more complicated, especially in areas with difficult terrain. Expanding infrastructure to facilitate transportation can increase project costs.
- Storage and transmission issues: Since wind power production is variable, efficient energy storage or a strong grid connection is necessary to ensure continuous electricity supply. However, energy storage technologies, such as batteries, remain costly, and upgrading transmission networks to connect wind farms to population centers is a major challenge.
3. Wind turbines for wind energy generation
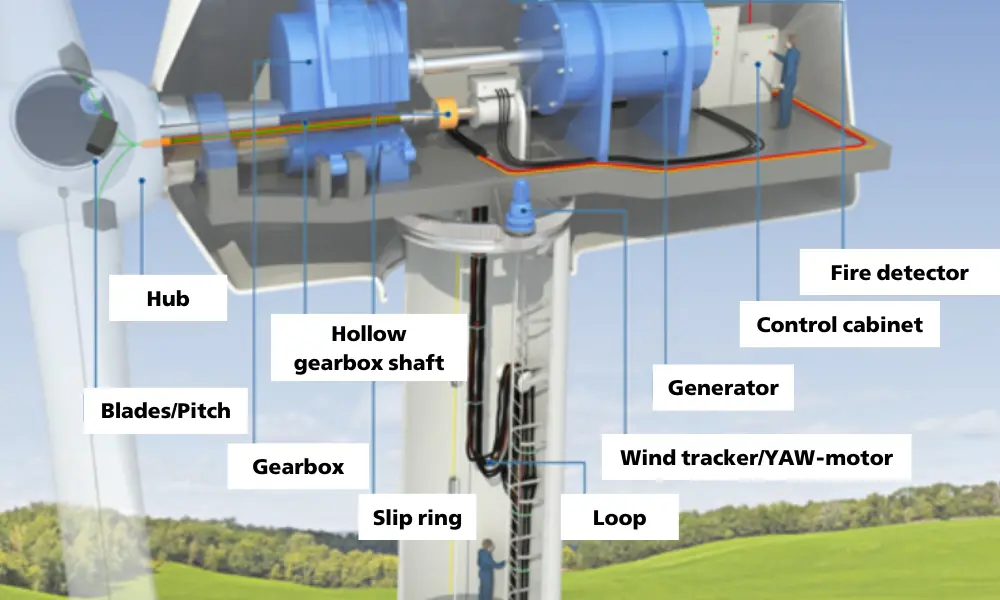
To harness wind energy, wind turbines must be installed and deployed.
3.1 Components of a wind turbine
A wind turbine consists of multiple components, with the key parts including:
- Nacelle: The outer casing of the wind turbine, which protects internal components such as the gearbox, generator, and yaw motor.
- Loop: A flexible electrical cable system that ensures adaptability to the turbine's movements during operation.
- Wind turbine tower: Supports the nacelle and must be anchored securely to the ground with a stable foundation to withstand loads.
- Other components: These include lift, cable connectors, and various support structures.
3.2 Horizontal axis vs. vertical axis wind turbines
Wind turbines come in various types, but the two most common are:
- Horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWT): The most widely used type, featuring a rotor with three or more blades that rotate around a horizontal axis perpendicular to the wind.
- Vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT): Designed with a rotor that rotates around a vertical axis, often featuring helical or egg-shaped blades. This compact and flexible design makes them suitable for limited spaces.
3.3 Operating principle of a wind turbine
Wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity using aerodynamic forces similar to airplane wings or helicopter blades. When wind flows across the turbine blades, air pressure on one side decreases, creating a pressure difference. This results in both lift and drag forces, with lift being stronger, causing the rotor to spin.
The rotor is connected to the generator in one of two ways:
- Direct drive turbines: The rotor connects directly to the generator.
- Gearbox turbines: A shaft and gearbox increase rotational speed, allowing for a smaller generator while maintaining sufficient electricity production.
This conversion of aerodynamic force into generator rotation is how wind turbines generate electricity. The constant movement and mechanical stress, combined with harsh environmental conditions, create significant challenges for the electrical cables used in wind turbines. These cables must withstand high temperatures, corrosion, twisting, and repetitive motion - requirements that HELUKABEL's specialized cables are designed to meet.
4. Current status and development potential of wind energy in Vietnam

In recent years, Vietnam has made significant progress in renewable energy, particularly in wind power. According to Power Development Plan VIII, the country aims to develop approximately 6,000 MW of offshore wind power capacity by 2030.
Despite challenges related to policies, infrastructure, electricity market mechanisms, and licensing procedures, wind energy remains a promising sector with the potential to make substantial contributions to Vietnam’s renewable energy portfolio. Many coastal provinces in Vietnam possess high potential for wind energy development, particularly in the following regions:
- Central coastal areas, including Ninh Thuan, Bình Thuan, Phu Yen, Quang Nam, and Quang Ngai.
- Southern coastal areas, such as Ba Ria – Vung Tau, Binh Phuoc, Kien Giang, and Ca Mau.
- Northern coastal areas, including Quang Ninh, Nam Đinh, Thai Binh, and Hai Phong.
5. HELUKABEL product portfolio for the wind energy sector
To ensure efficient and safe operation of wind power projects, electrical cables play a crucial role in transmitting electricity from wind turbines to the national grid. HELUKABEL is proud to provide high-quality cable solutions that meet international standards for the renewable energy sector.
Key HELUKABEL’s cables for wind power projects:
- Aluminum power cables: 0,6/1kV – 1,8/3kV: WK POWERLINE ALU, WK POWERLINE ALU robust, WK POWERLINE ALU halogen-free, NAYY, NA2Y, NA2XY
- Data cables: PAAR-TRONIC-CY, SUPERTRONIC®-PURö, SUPERTRONIC®330-C-PURö, SUPER-PAAR-TRONIC 340-C-PUR
- Control cables: JZ-500-HMH, H07RN-F, SOOW, HELUTHERM® 145 MULTI-C, TOPFLEX® 650 VFD, TRAYCONTROL® 600-C
- Communication cables: HELUKAT® PROFInet B CAT.5e SF/UTP PVC FLEX, HELUKAT® 100IND CAT.5 WK SF/UTP X-FRNC FLEX, Profibus SK
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |








