The importance of conductor cross-section in industrial applications
Why do cables come in different sizes? What are the influential factors that affect proper conductor cross-section selection? Let’s find out through the following article!
In industries, maintaining the consistent harmony of electrical systems is crucial for ensuring operational productivity and the safety of electrical systems and machinery. Proper conductor cross-section is fundamental to achieving this integration and involves a systematic approach to meet the essential needs of industries.
>>See more: Common types of industrial cables
1. A glance at conductor cross-section

Electric cables are the components that bind all parts of an electrical system together. They transmit energy from the power source to distribute it to equipment and machinery systems. However, one of the most common mistakes when installing cables is choosing cables that are either undersized or oversized.
Proper cable installation primarily involves sizing the cables correctly, using the right tools to attach the terminals, and providing adequate overcurrent protection with fuses and circuit breakers. Determining the appropriate conductor cross-section involves considering the cable length from the power source to the device and the current that will flow through it.
The longer the cable or the higher the amperage is, the larger the conductor cross-section must be to avoid unacceptable voltage losses. It's important to include an additional safety margin because the device may draw more current than its rating due to factors like heat, low voltage, or varying load. While oversized cables may not affect performance, undersized cables can pose serious electrical safety hazards.
>>See more: A guide to identify the quality of cables
2. The significance of conductor cross-section

2.1 Performance optimization
Industrial electrical systems require optimization through careful consideration of electrical conductor cross-sections for specific applications to operate efficiently and effectively. Power loss and voltage drop due to undersized cables and increased resistance can negatively impact the overall performance of equipment and machinery. Excessive voltage drop can hinder equipment performance and reliability. Controlling and minimizing voltage drop within allowable limits depends on selecting the appropriate conductor cross-section. Correct conductor cross-section addresses voltage drop concerns, improving machine longevity and performance.
Therefore, using electric cables of the appropriate size ensures a smooth and uninterrupted electricity transmission process. This also helps prevent potential breakdowns and enhances machine productivity.
2.2 Cost optimization
Choosing the right conductor cross-section helps save on initial investment costs. Oversized cables are much more expensive than cables that are correctly sized for your needs. Additionally, the size of electric cables significantly affects energy efficiency, which is the foundation of modern industrial operations. Inefficiently sized cables lead to power loss, which generates more heat and wastes energy.
2.3 Ensuring the safety of the electrical system
The purpose of any electrical cable is to transmit electrical energy over a certain distance with minimal resistance. The greater the need to transmit energy and connect devices, the larger the conductor cross-section should be. If a cable that is too small is used, the wire can become damaged, and the insulation sheath can melt because the current flowing through the wire is larger than its rated capacity. The smaller the diameter, the higher the resistance to energy flow. High resistance generates heat, increasing the risk of fire and explosion. Therefore, selecting the correct electric conductor cross-section is crucial for minimizing potential dangers and protecting both the workforce and the assets of the business.
>>Find out more: A glance at insulation resistance
2.4 Ensuring the longevity of electric cables
If the conductor cross-sections are incompatible with specific application, they can generate excessive heat that can destroy sensitive parts, thereby reducing the lifespan of machinery. Properly installed cables ensure that equipment operates under normal working conditions without undue strain or potential damage.
By correctly sizing cables to extend their lifespan, businesses can avoid disruptions due to downtime and maintenance, while also fortifying their infrastructure against unexpected events. This approach provides strategic benefits through extended reliability, increased equipment longevity, and guaranteed smooth operations.
2.5 Standards and regulations compliance
In industrial environments, compliance with standards is fundamental, and meeting administrative prerequisites through proper cable sizing is an important part of this process. For example, according to Vietnamese National Standard TCVN 9208:2012 on "Installation of cables and wires for industrial projects", the size of electric cables is specified as follows:
| Insulation | Armour | Diameter of the cable (mm) | Minimum bending radius |
| Rubber or PVC insulation with multi-strand copper or aluminum core | Unarmoured | Up to 10 | 3 |
| From 10 to 25 | 4 | ||
| Rubber or PVC insulation with multi-strand copper or aluminum core | Unarmoured | Larger than 25 | 6 |
| Steel wire armour | Any | 6 | |
| PVC insulation with solid copper or aluminum core | Steel wire armour or unarmoured | Any | 6 |
| Insulation with oil-soaked paper | Lead armour | Any | 6 |
| Insulation with inorganic substances | Copper or aluminum with/without PVC | Any | 6 |
3. Factors affecting conductor cross-section selection
When choosing conductor cross-section for specific applications, users need to pay attention to the following factors:
3.1 Installation method
This is the first thing to consider because how and where the cable is installed will directly affect whether the cable can be overloaded (for example, in a conduit, on a cable tray, free-standing installation). In general, the more confined the space you choose for cable installation (for example, in a duct versus a free-standing installation), the larger the conductor cross-section you need to use to ensure to avoid current attenuation, and that the installation distance (the gap) between the cables must be reasonable in order not to affect the power transmission performance.
>>See more: Top 4 halogen-free cables for outdoor use
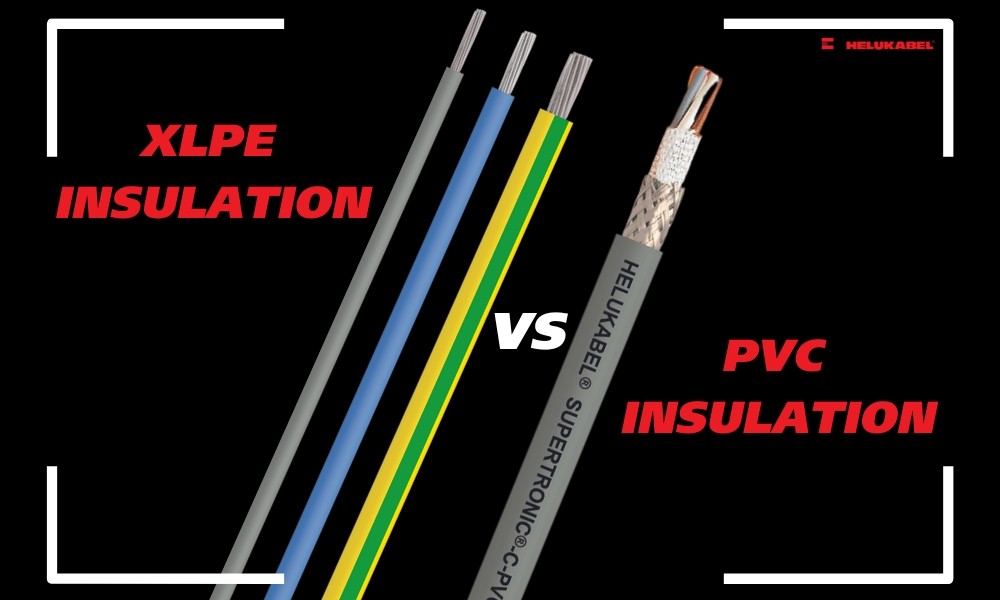
3.2 Insulation sheath
Insulation sheath is crucial in determining the conductor cross-section since it directly affects the maximum operating temperature of the cable. Common types of insulation material include PVC, XLPE, EPR rubber.
The maximum operating temperatures of PVC, XLPE, and EPR rubber are 70˚C, 90˚C and 90˚C, respectively. Though a lower operating temperature material, PVC is the more optimal choice in some cases. This involves other material properties that perform better in your installation environment. For example, PVC is much more flexible than XLPE and may be a better choice when you require cables to bend in tighter spaces.
You can also opt for either single-core cables or multi-core cables depending on the installation requirements, which will also affect the current-carrying capacity of the cable. Single-core cables can dissipate heat better than multi-core cables and will therefore be able to carry higher currents. However, the latter would be a great fit since it may be easier to install the necessary conductors.
>>See more: Comparing PVC and LSZH cables
3.3 Cable length
Ensuring transmission lines receive optimal voltage with minimal voltage drop is important. Smaller diameter cables inherently have higher resistance, leading to increased voltage drop. Therefore, choosing a cable that minimizes voltage drop is essential. Conductor cross-section and length primarily determine the circuit's voltage drop. The smaller the conductor cross-section or the longer the cable length required for your circuit, the greater the voltage drop.
>>See more: What is awg? Common awg cables
3.4 Derating factors
The current rating, or cable ampacity, can be affected by external factors, requiring the use of derating factors for accurate calculations. The key derating factors important for conductor cross-section include:
- Temperature Derating Factor (CT): Guided by standards such as IEC 60287 and NEC 310.16, the temperature derating factor accounts for the arrangement of cables to enhance heat dissipation. This factor is crucial for improving cable ampacity by considering the spatial arrangement for better heat loss mitigation.
- Conductor Grouping Factor (CG): According to standards like IEC 60287 and NEC 310.16, the electromagnetic field around grouped conductors reduces cable ampacity. The conductor grouping factor is introduced to address this effect and ensure accurate conductor cross-section selection.
- Thermal Resistivity of Soil (CR): Recognizing that cables buried in soil experience temperature variations, standards such as IEC 60287 and NEC 310.16 incorporate the thermal resistivity of soil factor. This factor compensates for temperature increases, enabling precise calculations.
- Burial Depth Derating Factor (CD): Influenced by standards like IEC 60287 and NEC 310.16, the burial depth derating factor comes into play based on the depth of conductor burial. Deeper burial increases the derating factor, necessitating careful consideration in conductor cross-section calculations.
4. Common conductor cross-sections from HELUKABEL
4.1 HELUKABEL’s 16 AWG cables
16 AWG cables, equivalent to a core size of about 1.5 mm2, are one of the common and widely used cable sizes.


JZ-600 PUR control cable
JZ-600 PUR control cable is extremely robust, exhibiting various outstanding characteristics such as abrasion resistance, ultraviolet rays’ resistance, mineral oils and coolant emulsions resistance. As a result, JZ-600 PUR control cable finds applications in tool machinery, conveyor belts and production lines, for plant installations, air conditioning and in steel production plants and rolling mills.
TOPSERV® 650 VFD
TOPSERV® 650 VFD cable is a highly flexible, extremely oil-resistant motor supply cable for modern servomotors; the tinned copper braid screen (approximately 85% coverage) provides effective protection against electrical disturbances and the resultant failures. For open, unprotected installation in cable trays and from cable trays to the machine. The special TPE sheath is extremely resistant to oil, coolants and solvents and hence the perfect solution for industrial applications with open installation, installation in pipes or in earth. In addition, TOPSERV® 650 VFD cable is suitable for use in drag chains.

4.2 HELUKABEL’s 18 AWG cables
HELUCHAIN® MULTIFLEX 512®-C-PUR UL/CSA
HELUCHAIN® MULTIFLEX 512®-C-PUR UL/CSA - UL/CSA approved drag chain cable for use in machine and tool manufacturing, in robotics and in other constantly moving machine parts; for permanently flexible applications moving freely without tensile stress and without movement control in dry, damp and wet rooms as well as outdoors. A slippery PP core insulation, cut-resistance and a low-adhesion PUR outer sheath guarantee optimum durability and excellent cost-efficiency.
Data sheet of HELUCHAIN® MULTIFLEX 512®-C-PUR UL/CSA - UL/CSA
HELUDATA® PLTC UL13 XLPE/LS0H OS 300
HELUDATA® PLTC UL13 XLPE/LS0H OS 300 is an LS0H cable, resistant to hydrocarbons, low level of line attenuations and low mutual capacitances enable long transmission distance. Moreover, components are produced of non-hygroscopic materials. Thus, this instrumentation cable is used for the transmission of digital and analog signals in harsh environments like oil, gas and petrochemical industries. The cable is suitable for fixed installation in dry and damp locations, open spaces and in underground networks.
TRAYCONTROL® 500
HELUKABEL® TRAYCONTROL® 500 is a flexible, oil-resistant control cable. The special combination of TC-ER, PLTC-ER and ITC-ER allows this cable to be used as a connecting cable for industrial plants and machinery in accordance with NFPA 79. Its outstanding oil resistance (OIL RES I & II) guarantees a long service life for industrial applications in dry, damp and wet environments. Recommended applications: production lines, bottling plants, machine construction, switch cabinets, conveyor systems, packaging machines, automotive industry.

If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
Tel. +84 28 77755578 | info@helukabel.com.vn | www.helukabel.com.vn